Introduction
In today’s digital age, where data collection and online privacy are hot topics of discussion, individuals need to understand their rights and options when it comes to opting out of data sharing and targeted advertising. In the United States, various opt-out requirements and mechanisms exist under different privacy laws at the federal and state levels.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key concepts, regulations, and best practices related to opt-out requirements in the US, including the types of data covered, opt-out mechanisms, notice requirements, consent models, and further guidance for businesses and consumers.
Understanding opt-out requirements
Opt-out requirements allow individuals to request that their personal information not be shared, sold, or used for specific purposes without their explicit consent. These requirements are aimed at protecting individuals’ privacy and giving them control over their personal data.
In the US, opt-out requirements are regulated by various federal and state laws, including the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA), the CAN-SPAM Act, and the Colorado Privacy Act, among others.
Types of data covered
Opt-out requirements typically apply to different types of personal information collected or processed by businesses and organizations. This includes but is not limited to:
Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
PPI includes information such as name, address, phone number, email address, social security number, and other similar information that can be used to identify an individual.
Sensitive personal information
Sensitive personal information includes information that is considered more sensitive, such as financial information, health information, sexual orientation, religious beliefs, racial or ethnic origin, and other similar data.
Personal information collected online
Personal information collected online includes data collected through online services, such as cookies, IP addresses, browsing history, geolocation data, and other similar information.
Data collected from children
Special requirements apply to data collected from children under the age of 13, including obtaining parental consent in compliance with the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).

Opt-out mechanisms
Opt-out mechanisms are the processes or methods businesses and organizations must provide to individuals to exercise their right to opt out of data sharing or targeted advertising. These mechanisms can vary depending on the applicable privacy laws and the type of data being processed. Some common opt-out mechanisms include:
Opt-out notice
Businesses must provide individuals with clear and conspicuous notice about their opt-out rights, including the types of data being collected, the purposes of data processing, and the right to opt-out of data sharing or targeted advertising.
Opt-out request form
Businesses must provide individuals with a simple and easy-to-use opt-out request form or mechanism, such as an online form, email address, or toll-free phone number, to submit their opt-out requests.
Global Privacy Control (GPC)
The GPC is a privacy signal that users can set in their web browser or device settings to indicate their preference to opt-out of data sharing or targeted advertising across different websites and online services.
Do Not Track (DNT) signals
DNT signals are browser settings that users can enable to indicate their preference to opt-out of data collection and targeted advertising. However, businesses are not legally required to honor DNT signals under current US privacy laws.
Privacy settings
Businesses must provide individuals with privacy settings or preferences within their online services to allow users to manage their data sharing and advertising preferences.
Notice requirements
Notice requirements are an essential aspect of opt-out requirements. They ensure that individuals are informed about their rights and options for opting out of data sharing or targeted advertising. Businesses and organizations are required to provide clear and conspicuous notice to individuals regarding their opt-out rights. Some common notice requirements include the following:
Privacy notice
A privacy notice, also known as a privacy policy, is a written statement that outlines how a business collects, uses, shares, and protects personal information, as well as the opt-out mechanisms available to individuals. The privacy notice must be easily accessible, written in plain language, and updated regularly to reflect any changes in data practices.
Opt-out notice
An opt-out notice is a specific type of notice that informs individuals about their right to opt-out of data sharing or targeted advertising and provides instructions on how to exercise this right. The opt-out notice must be provided during data collection through a clear and conspicuous link or button and be easily understandable.
Just-in-time notice
A just-in-time notice is displayed to users at the point of data collection or targeted advertising, providing them with an immediate opportunity to opt-out. Just-in-time notices are often used in mobile apps, online ads, or other interactive interfaces to obtain consumer consent and ensure that individuals are informed of their opt-out rights at the relevant moment.
Enhanced notice for sensitive information
For sensitive personal information, businesses may be required to provide enhanced notice, such as a separate notice or additional layers of notice, to highlight the sensitivity of the data and the importance of opting out of its use or disclosure.

Consent models
Consent models refer to the different approaches or frameworks for obtaining individuals’ consent for data sharing or targeted advertising. In the US, consumer consent models can vary depending on the applicable privacy laws and the type of data being processed. Some standard consent models include:
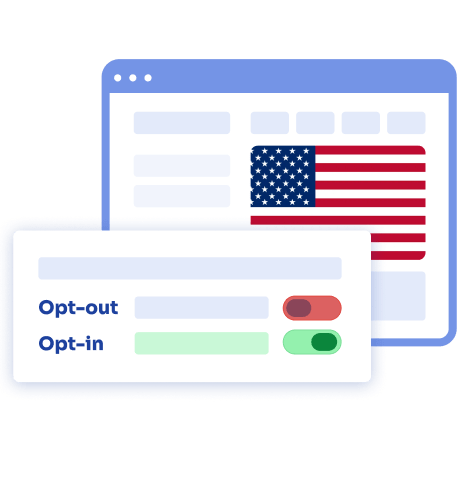
Opt-in consent
Opt-in consent requires individuals to actively provide their explicit consent, usually through positive action, such as checking a box or clicking a button, to indicate their agreement to data sharing or targeted advertising. Opt-in consent is often considered the strictest form of consent and is typically required for sensitive personal information, financial information, or data sharing with third parties.
Opt-out consent
Opt-out consent, on the other hand, assumes individuals’ consent by default unless they explicitly indicate their objection or opt-out of data sharing or targeted advertising. Opt-out consent is often used for less sensitive information. Individuals are typically provided with the option to opt-out through the opt-out mechanisms discussed earlier in this article.
Explicit consent for sensitive data
Some privacy laws, such as the GDPR and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), require explicit consent for processing sensitive personal information, which goes beyond regular opt-in or opt-out consent. Explicit consent may require individuals to provide their consent in a more detailed and specific manner, such as through a written statement, a signed consent form, or other similar means.
Further guidance for businesses and consumers
Businesses and organizations should follow best practices and seek legal counsel to ensure compliance with the opt-out requirements in the US. Some additional guidance for businesses includes:
Implementing robust opt-out mechanisms
Businesses should ensure their opt-out mechanisms are user-friendly, easily accessible, and effectively honor individuals’ opt-out requests on time. This may include providing multiple options for opting out, such as through online forms, email, phone, or other means, and regularly testing and monitoring the functionality of these mechanisms.
Providing clear and conspicuous notice
Businesses should provide clear and conspicuous notice to individuals about their opt-out rights, including privacy notices, opt-out notices, just-in-time notices, and other means. The notice should be written in plain language, easily understandable. It should clearly explain the purpose of data sharing or targeted advertising, the types of data collected and shared, and the available opt-out mechanisms.
Maintaining a record of opt-out requests
Businesses should maintain records of all opt-out requests received, including the date, time, and method of the request, as well as any relevant details, such as the specific data or advertising being opted out of. These records can serve as evidence of compliance in case of any legal disputes or regulatory audits.
Regularly reviewing and updating privacy policies
Privacy policies should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that they accurately reflect the business’s data collection, use, and sharing practices and the available opt-out mechanisms. Any changes to the privacy policy should be clearly communicated to individuals through updated notices and opt-out mechanisms.
Providing training and education to employees
Businesses should provide training and education to employees who handle personal information or interact with individuals regarding opt-out requests. This may include training on privacy laws, opt-out requirements, and best practices for managing opt-out requests consistently and competently.
Educating consumers about opt-out rights
Consumers should be educated about their opt-out rights and how to exercise them. Businesses can provide clear and understandable information about opt-out mechanisms through their privacy notices, websites, or customer service channels. Additionally, companies should respond promptly and professionally to consumer inquiries or requests related to opt-out rights.

Conclusion
Opt-out requirements are an important aspect of data privacy laws in the US aimed at protecting individuals’ privacy rights. These requirements, established through various privacy laws such as the CCPA, GDPR, FCRA, TCPA, CAN-SPAM Act, CPRA, and CPA, among others, allow individuals to control how their personal information is used for targeted advertising or shared with third parties.
As individuals become more aware of their privacy rights, businesses and organizations must prioritize compliance with opt-out requirements to build trust with their customers. By providing clear and conspicuous notice, implementing effective opt-out mechanisms, maintaining records of opt-out requests, regularly reviewing and updating privacy policies, training employees, and enlightening consumers about their opt-out rights, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to protecting individual privacy.
In a world where data privacy is a growing concern, businesses that proactively embrace opt-out requirements and ensure compliance will likely gain a competitive advantage. By respecting individuals’ privacy choices, companies can build customer loyalty, enhance their brand reputation, and foster trust among consumers. Compliance with opt-out requirements is not only a legal obligation but also a strategic business imperative in today’s privacy-conscious landscape. By prioritizing individual privacy rights, businesses can uphold ethical data practices, foster customer trust, and contribute to a more privacy-aware digital ecosystem.