Introduction
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has revolutionized how organizations handle personal data within the European Union. Central to the GDPR framework is the concept of the data controller, a key entity responsible for ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
Understanding the role and responsibilities of a data controller is crucial for businesses operating in the digital landscape. Whether you are an e-commerce platform, a marketing agency, or a subscription service, if you collect and process personal data, you likely fall under the category of a data controller.
In this article, we will delve into the definition of a data controller, explore their key responsibilities under the GDPR, and provide actionable insights to help you navigate the complexities of data protection compliance.
What is a Data Controller?
A data controller is an individual or organization determining the purposes, conditions, and means of processing personal data. In essence, data controllers are the key decision-makers when it comes to the collection and use of personal information. They are primarily responsible for ensuring that data processing activities comply with GDPR requirements.
Under the GDPR, data controllers must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data and enable individuals to exercise their data privacy rights. This includes obtaining valid consent, providing transparent information about data processing, and facilitating data subject requests.
Examples of data controllers
Businesses, organizations, and individuals who collect and use personal data for their own purposes are typically considered data controllers. Some common examples include:
E-commerce websites: Online stores that collect customer information for order processing, personalized product recommendations, and marketing purposes act as data controllers.
Social media platforms: Social networking sites that gather user data for advertising, friend recommendations, and content personalization are data controllers.
Marketing agencies: Agencies that collect and process data to create targeted advertising campaigns and reach potential customers on behalf of their clients are data controllers.
Subscription services: Platforms that offer subscription-based services, such as streaming media or software-as-a-service (SaaS), and collect user data for billing and content personalization are data controllers.
It is important to note that an organization can be both a data controller and a data processor, depending on the specific context and nature of the data processing activities. For example, a cloud storage provider may act as a data processor when storing customer data on behalf of a controller but as a data controller when collecting and using customer information for its own marketing purposes.
Key Responsibilities of Data Controllers
Determining the legal basis for processing
One of the fundamental responsibilities of a data controller is to identify and document a valid legal basis for processing personal data. The GDPR provides six lawful bases for processing:
Consent: The data subject has given explicit consent to process their personal data for one or more specific purposes.
Contract: Processing is essential for fulfilling a contract involving the data subject, or to act upon the data subject’s request prior to entering into a contract.
Legal obligation: The processing is necessary for compliance with a legal obligation to which the controller is subject.
Vital interests: The processing is necessary to protect the vital interests of the data subject or another natural person.
Public interest: Processing is required to carry out a task for the public interest or to exercise the official authority assigned to the controller.
Legitimate interests: Processing is required to serve the legitimate interests of the controller or a third party, unless these interests are overshadowed by the fundamental rights and freedoms of the data subject.
Data controllers must carefully assess which legal basis applies to their processing activities and ensure that they can demonstrate compliance with the chosen basis. When relying on consent, controllers must ensure it is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Data subjects must also be able to withdraw their consent easily at any time.
Implementing data protection principles
Data controllers are responsible for implementing and adhering to the key data protection principles outlined in the GDPR:
Data minimization: Controllers should collect only the personal data necessary for the specified purposes. They must ensure that the data collected is adequate, relevant, and limited to what is required.
Purpose limitation: Personal data must be gathered for clear, specific, and valid reasons and should not be processed further in ways that contradict those reasons.
Accuracy: Controllers must take reasonable steps to ensure that their personal data is accurate and, where necessary, kept up to date. Inaccurate data should be rectified or erased without delay.
Storage limitation: Personal data must be retained in a way that allows for the identification of data subjects only as long as is necessary for the intended processing purposes.
Integrity and confidentiality: Controllers are required to adopt suitable technical and organizational safeguards to secure personal data against unauthorized access, modification, disclosure, or destruction.
To demonstrate compliance with these principles, data controllers should maintain detailed records of their processing activities, conduct regular data protection impact assessments (DPIAs), and implement robust security measures—such as encryption, pseudonymization, and access controls.
Providing transparency and information to data subjects
Transparency is a core principle of the GDPR, and data controllers play a crucial role in ensuring that data subjects are well-informed about processing their personal data. Controllers must provide clear, concise, and easily accessible privacy notices to individuals at the time of data collection.
Privacy notices should include the following information:
The identity and contact details of the data controller
The purposes of the processing and the legal basis for processing
The categories of personal data concerned
The recipients or categories of recipients of the personal data
The retention period or criteria used to determine the retention period
The existence of data subject rights, such as the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, object to processing, and data portability
The right to withdraw consent at any time (where applicable)
The right to lodge a complaint with a supervisory authority
The existence of automated decision-making, including profiling, and meaningful information about the logic involved and the significance and envisaged consequences of such processing for the data subject
Data controllers should regularly review and update their privacy notices to accurately reflect their processing activities and remain compliant with the GDPR. Tools like Pandectes‘ privacy policy generator can help streamline this process, ensuring your privacy notices are comprehensive and up-to-date.
Accountability and Compliance Measures
Maintaining Records of Processing Activities
Data controllers are obligated to keep meticulous documentation of their data processing operations. These records should detail the specific purposes of processing, categories of data subjects, and types of personal data processed, along with any entities that receive this data and the timeframes for its retention. Such thorough recording is evidence of compliance with GDPR mandates and is essential during audits or inquiries by data protection authorities, illustrating a transparent and accountable data management approach.
Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
When processing activities could significantly impact individuals’ privacy, conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) becomes crucial. DPIAs provide a framework for evaluating the potential privacy risks and developing strategies to mitigate them effectively. This forward-thinking process aligns with GDPR’s proactive risk management ethos and fosters trust by demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding personal data. Organizations can avert issues and bolster their data protection posture by identifying and addressing potential privacy concerns early.
Implementing Appropriate Technical and Organizational Measures
A robust security framework is vital for defending personal data against breaches and unauthorized access. Data controllers should deploy a combination of technological solutions, such as data encryption and access restrictions, to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Additionally, regular evaluations and updates to security protocols are necessary to adapt to evolving threats. By integrating these defensive measures into their operations, organizations not only adhere to GDPR requirements but also reinforce their dedication to upholding high data privacy and security standards.
Managing Data Subject Rights
Facilitating the Exercise of Data Subject Rights
Data controllers must ensure that mechanisms are in place to address data subject requests with precision and efficiency. This encompasses facilitating access to personal data, correcting inaccuracies, executing deletion requests, and enabling data portability. Responses to such requests should occur within one month, though an extension of up to two months is permissible for particularly complex cases. To achieve this, controllers should implement streamlined procedures that facilitate seamless communication and processing, ensuring adherence to GDPR mandates while respecting individuals’ rights.
To enhance the efficiency of handling data subject requests, controllers can deploy advanced systems that simplify the submission and tracking process for individuals. These systems should provide users with clear instructions and real-time updates on the status of their requests. Leveraging technology to automate routine tasks can significantly reduce response times and improve accuracy, demonstrating a commitment to maintaining high data protection and transparency standards.
Handling Data Subject Complaints and Inquiries
Addressing complaints and inquiries with diligence is a fundamental duty for data controllers, reflecting their commitment to transparency and accountability. Establishing a dedicated channel for managing these concerns is essential and ensuring that data subjects have access to knowledgeable representatives who can provide timely and comprehensive responses.
In potential escalations involving supervisory authorities, data controllers must be prepared to furnish detailed records and insights into their data handling practices. By establishing open lines of communication and adopting a proactive approach to managing inquiries and complaints, organizations can reinforce their dedication to GDPR compliance and bolster stakeholder trust. Data controllers demonstrate their alignment with regulatory expectations and commitment to safeguarding individuals’ rights through meticulous documentation and responsive engagement.
Data Breaches and Notification Obligations
Detecting and Responding to Data Breaches
Data controllers must maintain vigilance in identifying and managing data breaches to protect personal data. Implementing advanced monitoring tools that provide continuous oversight and alert capabilities is essential. When a breach is suspected, it is imperative to conduct a detailed investigation to determine its scope and potential impact on data subjects. Rapid response is critical; thus, controllers should enact immediate measures to contain the breach, secure data systems, and prevent further unauthorized access.
Having an incident response plan is vital. This plan should delineate specific roles and responsibilities, establish clear communication channels, and outline technical remediation strategies. Such preparedness ensures a swift and coordinated effort to address breaches effectively.
Notifying Supervisory Authorities and Data Subjects
Under GDPR, data controllers must inform the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of identifying a data breach, highlighting the need for transparency and prompt action. The notification must encompass comprehensive details about the breach, including the type of data compromised, the number of affected individuals, and the potential risks the incident poses. Furthermore, controllers should describe the corrective actions taken to mitigate any adverse effects.
If a breach threatens individuals’ rights and freedoms, controllers are obligated to inform those affected promptly. This notification should be succinct yet informative, enabling individuals to comprehend the breach’s nature and its ramifications for their personal data. Additionally, it should provide practical advice on protective measures individuals can undertake, such as monitoring account activity or updating security credentials. By fulfilling these notification requirements, data controllers adhere to GDPR mandates and underscore their dedication to upholding data privacy and security.
Engaging Data Processors and Third Parties
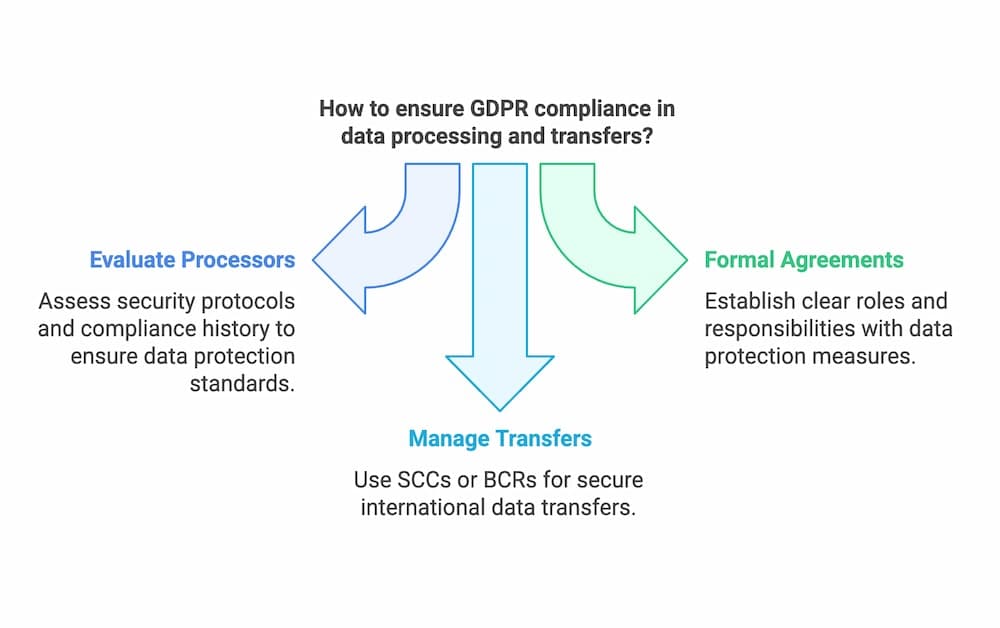
Selecting GDPR-Compliant Data Processors
When selecting data processors, data controllers must ensure that the chosen partners can uphold stringent data protection standards as GDPR requires. This involves conducting comprehensive evaluations of the processor’s security protocols, compliance history, and capacity for maintaining data confidentiality. Controllers should prioritize processors demonstrating a robust commitment to safeguarding personal data through proven methodologies and practices.
Establishing a formal agreement between the controller and processor is crucial to delineate the parameters of data processing activities. This agreement should detail the nature and duration of processing and delineate both parties’ specific roles and responsibilities. Essential elements include stipulations for data protection measures, protocols for addressing data subject requests, and procedures for incident reporting. Controllers clearly define these contractual obligations and ensure processors remain aligned with GDPR compliance standards.
Managing Data Transfers and International Data Flows
In global operations, data transfers across borders present unique challenges that require meticulous management. Data controllers must ensure that any transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA) adheres to GDPR requirements. This often involves employing mechanisms such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) to secure legal provisions for international data transfers.
SCCs function as predefined contractual frameworks that enforce data protection obligations on both parties involved in the transfer. These clauses provide a structured approach to maintaining data security during cross-border transfers. Similarly, BCRs offer internal corporate policies that multinational companies can adopt to facilitate secure data transfer within their group. Additionally, controllers may rely on adequacy decisions, where the European Commission recognizes that a third country offers sufficient data protection measures.
Effective management of data transfers necessitates continuous oversight and a proactive stance. Controllers should routinely assess and refine their data transfer strategies, integrating any updates in regulatory guidelines or international agreements. By implementing comprehensive mechanisms for data transfers, controllers can confidently engage with global partners while protecting personal data across jurisdictions.
Cooperating with Investigations and Audits
To comply with GDPR, data controllers must work closely with supervisory authorities during investigations and audits. This means granting access to facilities, documentation, and relevant data for thorough examinations, showcasing a commitment to transparency. A cooperative approach helps controllers address regulatory concerns and build a positive relationship with authorities. Controllers need to facilitate easy information exchange by keeping requested materials organized and accessible. Aligning internal processes with regulatory standards allows for efficient audits, minimizing disruptions, and reinforcing data protection commitments.
Implementing Recommendations and Corrective Measures
When receiving feedback or recommendations from authorities, data controllers must act quickly to close compliance gaps. This includes assessing issues and developing a targeted resolution plan while maintaining open communication with authorities to provide progress updates. Clear objectives and resource allocation are essential for implementing corrective measures effectively. Documenting the entire process supports internal compliance tracking and evidences the organization’s commitment to improving data protection practices. By decisively addressing recommendations, controllers can enhance their compliance framework and foster a culture of continuous improvement in data management.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of a data controller under the GDPR is essential for any organization that handles personal data. As the primary decision-makers in data processing activities, data controllers must navigate a complex landscape of legal obligations and ethical considerations. By clearly identifying the legal basis for processing personal data and implementing key data protection principles—such as data minimization and purpose limitation—businesses can ensure compliance and build trust with their users. As data privacy concerns continue to grow, embracing these responsibilities will be critical for fostering a secure and transparent digital environment. Ensuring compliance with GDPR protects individuals’ rights and enhances organizations’ reputation in a competitive marketplace.



