Introduction
South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) has garnered global attention since its enactment in 2011. Renowned for its stringent provisions and rigorous enforcement, PIPA stands as a cornerstone of data privacy legislation in Asia.
The law’s comprehensive scope encompasses a wide array of entities—from public institutions to private corporations and online service providers—underscoring South Korea’s commitment to safeguarding personal information across sectors. PIPA’s enactment marked a significant milestone in the nation’s endeavor to address the escalating challenges posed by the digital age.
As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, PIPA has adapted to keep stride, with periodic updates mandated by the Personal Information Protection Commission. These revisions ensure that the law remains relevant and effective in protecting individual rights in an ever-changing digital landscape.
- No coding required
- Works with all Shopify themes
- Blocks tracking before consent
- Google Consent Mode v2 ready
- Trusted by 173k+ stores
- 2,700+ 5-star reviews
- Google CMP Partner
What is South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA)?
The Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) of South Korea is an extensive data privacy law that was enacted in September 2011. It is widely regarded as one of the world’s strictest privacy laws, with penalties enforced enthusiastically by the regulatory authorities.
PIPA’s scope is extensive, applying to most organization types, including government entities, public institutions, and private businesses. This broad applicability underscores South Korea’s commitment to ensuring the protection of personal information across all sectors of society. Under PIPA, any entity that processes personal information is considered a personal information controller and must adhere to the law’s stringent requirements.
A key feature of PIPA is the requirement for periodic updates by the Personal Information Protection Commission. This provision ensures that the law keeps pace with the rapid advancements in technology, addressing emerging privacy challenges and maintaining its effectiveness in safeguarding individual rights in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
The amended PIPA, which entered into force on September 15, 2023, introduced several significant changes:
Streamlined dispute mediation procedures: Data processors are now obligated to participate in mediation, expediting the remediation process in cases of personal data infringement.
Unified standards for data processing: Online and offline data processing standards have been harmonized, subjecting all personal information processors to the same regulations, promoting fairness and consistency.
Enhanced breach notification requirements: Data breaches must be reported within 72 hours, a notable change from the previous version, which allowed controllers 5 days and information and communication service providers only 24 hours.
Strengthened safety measures in the public sector: The amended law introduces more robust measures to ensure the safe processing of personal information by public entities, bolstering public trust.
Alignment with global standards: The requirements for cross-border personal information transfers have been diversified, and the penalty system has been reorganized, bringing PIPA closer to international norms.
These amendments demonstrate South Korea’s ongoing commitment to refining its data protection framework, striking a balance between individual rights and the needs of businesses in an increasingly data-driven economy. By staying attuned to global developments and the evolving technology landscape, PIPA positions itself as a forward-thinking and adaptable law, well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the digital age.
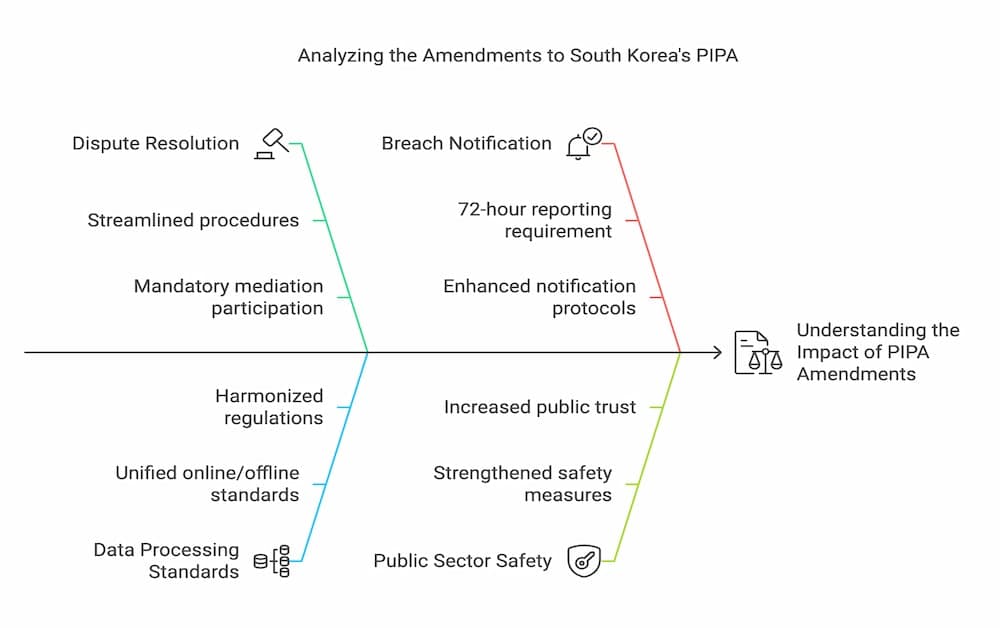
Key Amendments: 2020 and 2023 Updates
The 2020 amendment to PIPA marked a significant shift by introducing the concepts of pseudonymization and anonymization of data. This allowed for the processing of pseudonymous and anonymous data without the stringent restrictions applied to identifiable personal information, thereby facilitating data utilization while maintaining privacy. Additionally, the amendment implemented new requirements, restrictions, and penalties to enhance data protection.
The 2023 amendment further bolstered the law by expanding the rights of data subjects. Notably, it introduced the right to data portability, allowing individuals to transfer their data between service providers seamlessly. It also granted data subjects the right to be excluded from automated decision-making processes, providing a safeguard against potentially biased or unfair automated outcomes. Furthermore, the amendment set new requirements for overseas personal data transfer, ensuring that such transfers are conducted with adequate protections in place. Criminal sanctions were replaced with fines, aligning PIPA more closely with international data protection standards.
Key Definitions and Scope of PIPA
PIPA delineates a robust framework for personal information protection, encompassing data that directly identifies an individual as well as data that can do so when combined with other information. This expansive definition underscores the law’s intent to cover a broad spectrum of data categories, ensuring comprehensive protection across various data forms.
With regard to sensitive personal information, PIPA accords special attention to categories that could compromise individual privacy, such as ideological beliefs, union affiliations, political leanings, health details, and biometric identifiers. This focus necessitates a higher level of consent and security measures, reflecting the importance of safeguarding the most intimate facets of personal data.
In defining “processing,” PIPA captures a wide array of activities, including the acquisition, management, and eventual destruction of personal data, collectively referred to as personal information processing. This extensive definition ensures that every stage of the data lifecycle is subject to legal compliance, mandating that entities handling such data implement comprehensive oversight mechanisms.
Entities must ensure they have explicit consent from data subjects to process personal information, adhering to the legal frameworks established by PIPA.
Territorial Scope
PIPA’s reach extends beyond South Korea’s borders, akin to the GDPR, influencing organizations that process the data of South Korean individuals regardless of their geographical location. This extraterritorial scope mandates compliance from any entity engaging with South Korean residents, reinforcing the law’s global significance in efforts to protect personal data.
Exclusions from PIPA
Despite its broad application, certain categories of data fall outside PIPA’s jurisdiction—such as information collected for reasons of national security or public safety and data handled by press, religious, or political entities. These exclusions acknowledge the unique operational needs of these sectors, allowing them to function effectively while maintaining a balance with privacy considerations.
Data Protection Officers (DPOs) and Their Role
Under PIPA, every personal data controller is required to designate a Chief Privacy Officer (CPO) to ensure compliance with the law. The CPO must be an employee or executive of the organization with at least three years of experience in personal information protection. The responsibilities of the CPO are extensive and include guaranteeing access to all information related to the processing of personal information, establishing a system for direct reporting to the representative and the board of directors, and providing the necessary human and material resources to perform their duties effectively. This role is crucial in maintaining the integrity of personal data processing activities and ensuring that the organization adheres to PIPA’s stringent requirements.
Facilitating Compliance with PIPA
To effectively adhere to South Korea’s PIPA, organizations must integrate the foundational principles that govern data processing activities. These include clearly defining the specific purposes for data collection and processing and ensuring data is collected only as necessary to fulfill those objectives. Furthermore, maintaining data integrity through regular updates and verification processes is essential to prevent inaccuracies that could compromise privacy. Obtaining the data subject’s consent is crucial for lawful data processing under PIPA, ensuring that individuals are aware of and agree to how their information is used.
Robust security protocols are vital for safeguarding personal data under PIPA, which aims to protect personal information from breaches, unauthorized access, or alterations. Organizations should implement a mix of technical, managerial, and physical measures to shield data from breaches, unauthorized access, or alterations. This involves adopting advanced technologies, such as encryption and secure access systems, alongside regular security audits to identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities.
A comprehensive privacy policy outlines an organization’s data handling practices and is crucial for PIPA compliance. This policy should transparently detail the types of data collected, the reasons for collection, and any data-sharing practices. It fosters trust and aligns with PIPA’s emphasis on accountability. Appointing a privacy officer is also critical, as this role involves overseeing compliance efforts and acting as a liaison between the organization and regulatory authorities.
Specific compliance strategies must also be considered. For example, when processing data of minors under 14 years, obtaining consent from a legal guardian is mandatory. This step emphasizes the safeguarding of minors’ data and requires clear communication with guardians about data practices. Conducting privacy impact assessments (PIAs) for activities carrying significant privacy risks is crucial, as these assessments help identify and address potential privacy concerns proactively.
In the event of a data breach, prompt notification is essential. Organizations are required to inform regulatory bodies and affected individuals swiftly, thus enabling proactive measures to safeguard personal information. Establishing a detailed incident response plan ensures that organizations can effectively manage breaches, mitigating potential damages while adhering to PIPA’s stringent requirements.
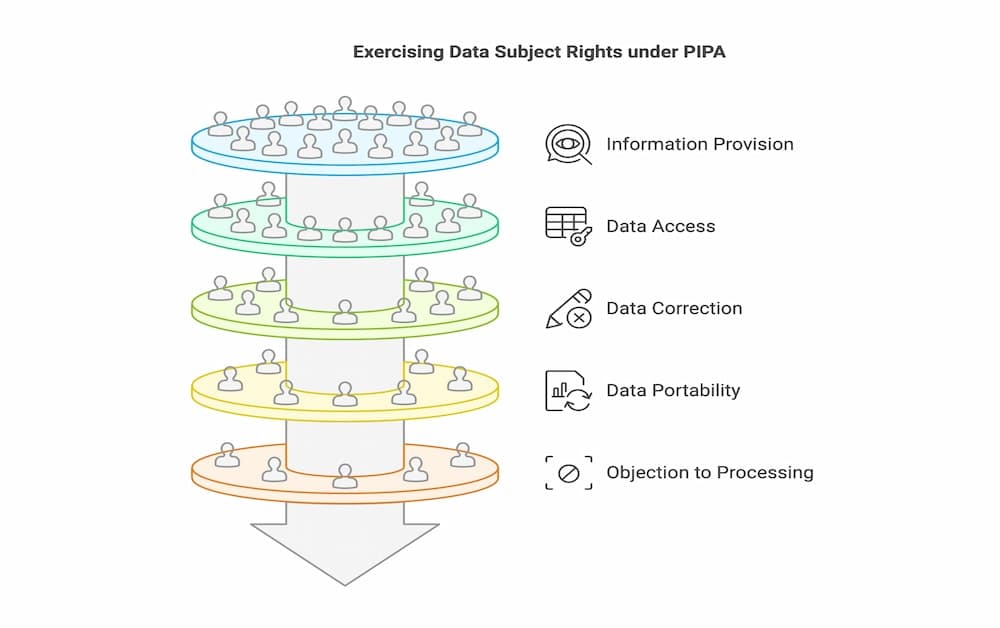
Data Subject Rights under PIPA
PIPA delineates specific rights for individuals, ensuring they retain control over their personal data. One of these rights is the entitlement to receive comprehensive information about how their data is processed. Organizations must clearly outline the purposes and methods of data processing, promoting an environment of transparency and trust.
Personal information controllers must ensure that data subjects can easily exercise their rights, promoting transparency and trust in data handling practices.
Another crucial aspect of PIPA is the right of individuals to access their personal data, allowing them to verify the accuracy and integrity of the information held. If discrepancies are found, individuals have the right to request corrections, deletions, or a halt in processing. This empowers them to maintain the accuracy and relevance of their data, reinforcing their autonomy in data management.
The law also enshrines the right to data portability, enabling individuals to transfer their data between service providers without hindrance. This provision ensures flexibility and control, allowing people to choose service providers that best meet their privacy needs. Additionally, PIPA grants individuals the right to object to certain data processing activities, including those involving automated decision-making, providing a safeguard against unwanted data practices.
PIPA establishes a clear process for exercising these rights, either directly with the organization or through the Personal Information Protection Commission. This dual mechanism ensures that individuals have both direct and oversight avenues to assert their rights, underscoring PIPA’s dedication to protecting personal privacy and fostering accountability in data handling practices.
Addressing Data Subject Access Requests
Effectively managing data subject access requests under PIPA necessitates a well-defined and efficient protocol that upholds compliance and strengthens trust with individuals. Organizations should design a transparent system that allows individuals to clearly specify the information they seek to access. This involves setting up a straightforward mechanism that guides individuals through the request submission process, ensuring it is both accessible and comprehensible.
A critical aspect of this process is the obligation to provide timely responses to access requests. PIPA stipulates that organizations must respond within a designated period, ensuring that data is delivered promptly and accurately. This necessitates maintaining streamlined internal operations that can handle requests swiftly. The data provided should be in a format that is easily understandable, reinforcing the organization’s commitment to transparency and user empowerment.
Ensuring that access request procedures are straightforward and not overly complex is essential. Organizations should aim to reflect the simplicity of their initial data collection processes, thereby avoiding unnecessary hurdles for individuals seeking their data. While organizations are permitted to impose fees for requests that exceed a set frequency, these should be reasonable and aligned with the actual administrative effort involved, ensuring that individuals can exercise their rights under PIPA without undue financial burden.
Data Breach and Security Measures
PIPA mandates that personal data controllers implement robust technical and administrative measures to prevent the loss, theft, leakage, alteration, or destruction of personal information. In the event of a data breach, the personal data controller must notify the affected data subjects within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach. Additionally, if the breach involves the personal information of 1,000 or more data subjects, sensitive information, unique identification information, or results from unauthorized external access, the data controller must report the incident to the regulator within the same 72-hour timeframe. These stringent requirements underscore the importance of prompt and transparent communication in mitigating the impact of data breaches and protecting personal information.
Cross-Border Data Transfer
PIPA sets stringent requirements for the international transfer of personal data, ensuring that such transfers are conducted with adequate protections in place. Personal data controllers must ensure that the recipient country has data protection laws that meet PIPA’s standards. Additionally, they must obtain the consent of data subjects before transferring their personal information to a third country. To further safeguard personal data during cross-border transfers, personal data controllers are required to implement data encryption and other security measures. These provisions ensure that personal data remains protected, even when transferred across international borders, aligning with global data protection practices.
• 7-day free trials on all paid features.
• No setup fees. Cancel anytime.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) can be a daunting task for businesses, but understanding how it protects personal information is crucial for compliance. However, by understanding the key provisions, implementing robust compliance strategies, and respecting data subject rights, organizations can ensure they meet the stringent requirements of this forward-thinking law. If you’re looking for a comprehensive solution to simplify your Shopify store’s compliance with GDPR and other global privacy regulations, try Pandectes GDPR Compliance, and let us help you build trust with your customers while focusing on growing your business.



