Introduction
With increasing concerns about data privacy, businesses must ensure they comply with evolving data privacy law regulations. The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), an enhancement of the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), imposes stricter requirements for obtaining and managing consumer consent. Transparency and consent are crucial when handling consumer data to build trust and avoid legal repercussions. As of 2025, companies must reassess their cookie consent practices to align with CPRA’s explicit consent rules, transparency standards, and opt-out mechanisms. The California Privacy Protection Agency plays a significant role in enforcing CPRA compliance. This article explores the key aspects of CPRA cookie consent compliance and how businesses can effectively implement these requirements.
Understanding CPRA and Its Impact on Cookie Consent
The CPRA strengthens consumer rights by expanding the definition of personal and sensitive information. It introduces stricter regulations for businesses handling user data, particularly through cookies used for tracking, analytics, and targeted advertising. Unlike the CCPA, which primarily allowed consumers to opt-out, the CPRA mandates explicit consent for certain types of data collection. Companies must ensure that their cookie consent banner provides clear, detailed information about the types of cookies used and gives consumers the choice to accept or reject them.
Data privacy laws in the United States are evolving, with state-level legislation granting consumers specific rights over their personal data. Businesses must comply with these laws to avoid legal repercussions and foster trust with consumers.
Under CPRA, organizations must also offer an accessible opt-out mechanism, allowing users to withdraw consent at any time. Businesses failing to comply risk enforcement actions, fines, and potential reputational damage. The focus is on consumer empowerment, ensuring users have full control over their personal data.
Key CPRA Cookie Consent Requirements
To comply with CPRA, businesses must implement the following:
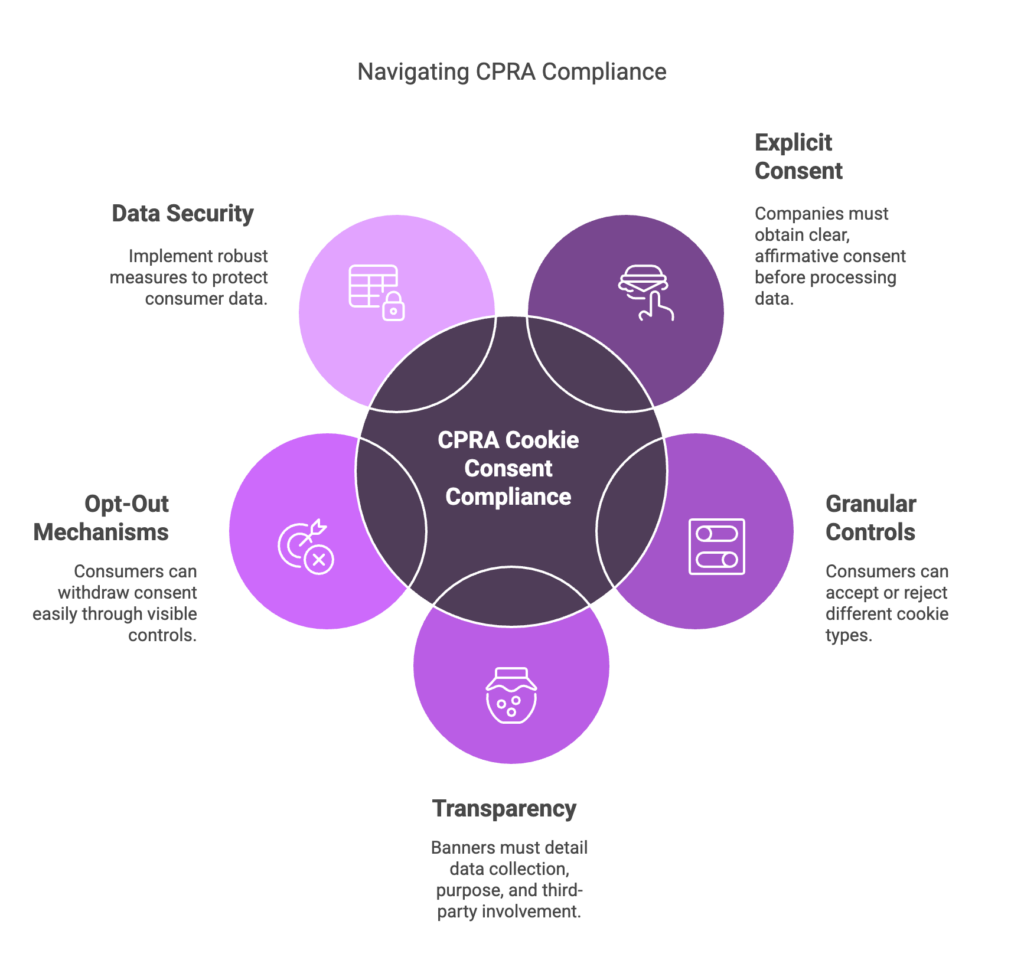
Explicit Consent for Data Collection – Companies must obtain clear, affirmative consent before processing sensitive personal information through cookies. Implied consent or pre-checked boxes are no longer sufficient.
Granular Opt-In and Opt-Out Controls – Consumers should have the option to accept or reject different types of cookies, including those used for essential site functionality, analytics, or targeted advertising.
Transparency in Data Collection – Cookie consent banners must provide concise yet comprehensive details on what data is collected, its purpose, and whether third-party cookies are involved. These banners enhance the credibility and professionalism of a website while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Easy-to-Access Opt-Out Mechanisms – Businesses must ensure that consumers can withdraw consent at any time through visible and user-friendly controls, such as a dedicated “Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information” link.
Universal Opt-Out Compliance – Companies must recognize and honor opt-out signals sent via Global Privacy Control (GPC) and similar technologies.
Robust Data Security Measures – Businesses must implement robust data security measures to comply with state privacy laws such as the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act and the California Privacy Rights Act. These measures protect sensitive consumer data, ensuring transparency and consumer rights in the handling of personal information.
Key Changes in Cookie Consent under CPRA
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) has introduced significant changes in cookie consent requirements, emphasizing user control and transparency. Here are the key changes businesses need to be aware of:
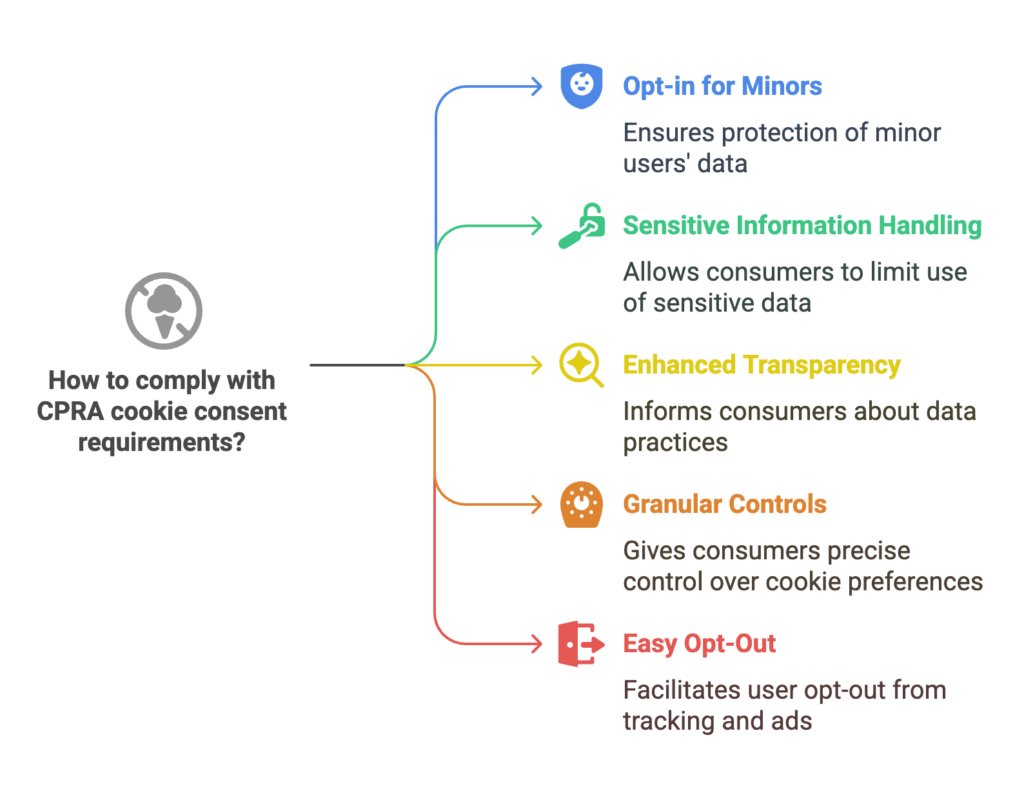
Opt-in Consent for Minors: Under the CPRA, businesses must obtain explicit consent from minors (below 16 years) before collecting, processing, or sharing their personal information. This ensures that younger users are protected and their data is handled with extra care.
Sensitive Personal Information: The CPRA introduces a new category of personal data known as sensitive personal information. This includes financial information, health information, and biometric data. Consumers now have the right to limit the use and sharing of this sensitive personal information, adding an extra layer of protection for their most private data.
Enhanced Transparency: Businesses are required to provide clear and concise information about their data collection practices, including the use of cookies and third-party cookies. This transparency helps inform consumers about how their data is being used and who it is being shared with.
Granular Controls: Consumers must be given the option to manage their cookie preferences with greater precision. This includes the ability to opt-out of specific types of cookies, such as those used for analytics or cross-context behavioral advertising, ensuring that users have more control over their personal data.
Easy Opt-Out: Businesses must provide a clear and easily accessible option for consumers to opt-out of personalized advertisements and tracking. This can be achieved through a prominent “Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information” link, making it simple for users to exercise their rights.
Handling Sensitive Personal Information
One of CPRA’s key additions is the category of sensitive personal information, which includes biometric data, health details, financial information, and geolocation data. For such data, businesses must secure explicit consent before processing it through cookies, in compliance with privacy law requirements.
Additionally, data security measures play a crucial role in protecting sensitive personal information. These measures are mandated by laws like the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act and the California Privacy Rights Act to ensure transparency and consumer rights in the handling of personal information.
Furthermore, CPRA mandates privacy risk assessments for handling sensitive data. Businesses should evaluate their data collection practices to ensure compliance and implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
Best Practices for CPRA-Compliant Cookie Consent
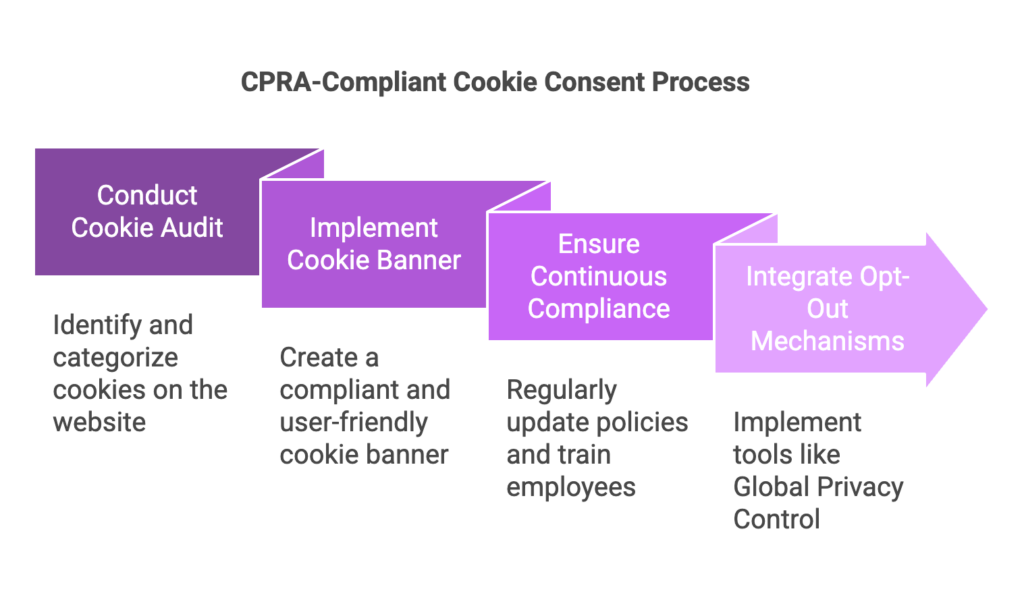
- Conduct a Cookie Audit
A thorough audit helps businesses identify which cookies are used on their websites, the data collection practices involved, and their necessity. This assessment enables companies to categorize cookies properly and ensure they comply with CPRA regulations.
- Implement a CPRA-Compliant Cookie Banner
A well-designed cookie banner should:
- Clearly state why cookies are used, what data they collect, and ensure that the cookie consent banners are customizable to match the brand’s identity while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like the CPRA.
- Offer granular control, allowing users to opt in or out of specific cookie categories.
- Avoid deceptive design practices (dark patterns) that could mislead users into consenting.- Provide a visible and accessible opt-out option.
- Ensure Continuous Compliance
CPRA compliance is not a one-time process. Businesses must:
- Update cookie policies regularly to align with changes in data processing and meet evolving data privacy regulations.
- Reassess consent mechanisms to ensure they remain transparent and effective.
- Train employees on privacy requirements to ensure company-wide adherence.
- Integrate Universal Opt-Out Mechanisms
To align with CPRA’s requirement to recognize opt-out signals, businesses should integrate tools such as Global Privacy Control (GPC). This allows consumers to set privacy preferences at the browser level, automatically applying them across multiple websites.
It is also crucial to respect consumer consent when integrating these universal opt-out mechanisms.
Managing User Preferences and Compliance
Managing user preferences and ensuring compliance with the CPRA can be complex, especially for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions. Here are some best practices to help navigate these challenges:
Implement a Robust Consent Management System: A comprehensive consent management system is crucial. This system should allow consumers to manage their cookie preferences easily and opt-out of data collection and processing. It should be user-friendly and integrated seamlessly into the website’s interface.
Conduct Regular Audits: Regular audits are essential to ensure that data collection and processing practices remain compliant with the CPRA. These audits help identify any gaps or areas for improvement, ensuring ongoing compliance and data protection.
Provide Clear and Concise Information: Transparency is key. Businesses must provide clear and concise information about their data collection practices, including the use of cookies and third-party cookies. This information should be easily accessible and understandable to all users.
Respect Consumer Choices: It’s vital to respect consumer choices and opt-out requests. Businesses must ensure that their data collection and processing practices align with consumer preferences and data privacy law, honoring their decisions to opt-out of certain types of data collection or sharing.
Enforcement and Consequences of Non-Compliance by the California Privacy Protection Agency
The California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) oversees CPRA enforcement and ensures compliance with privacy laws, issuing fines for violations. Businesses face penalties of up to $7,500 per intentional violation and $2,500 for unintentional infractions. Additionally, non-compliance risks consumer trust loss, leading to reputational damage and potential revenue decline. Ensuring robust data protection is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
To mitigate these risks, companies must proactively monitor compliance, address privacy concerns, and adopt transparent data-handling practices.
California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) Enforcement
The California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) is responsible for enforcing the CPRA. The CPPA has the authority to:
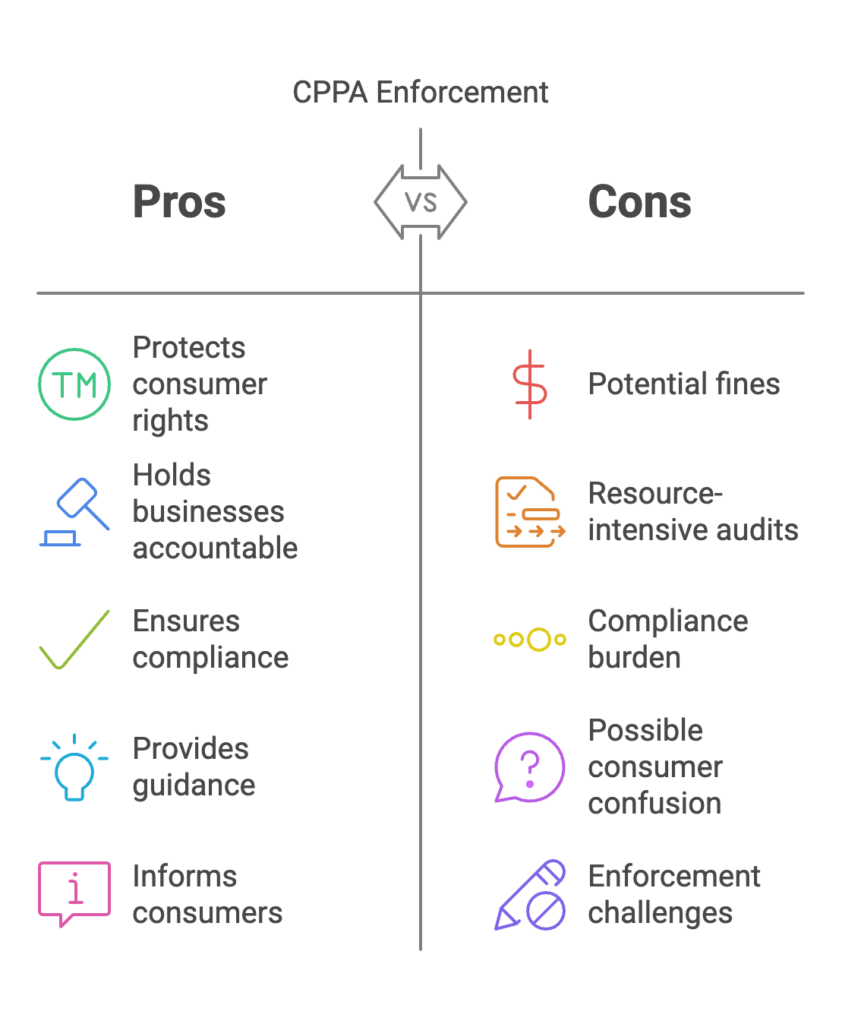
Investigate Complaints: The CPPA can investigate complaints and alleged violations of the CPRA. This ensures that consumer rights are protected and that businesses are held accountable for their data practices.
Impose Fines: The CPPA can impose fines and penalties for non-compliance with the CPRA. Businesses face penalties of up to $7,500 per intentional violation and $2,500 for unintentional infractions, making compliance a critical priority.
Conduct Audits: The CPPA has the power to conduct audits to ensure that businesses are compliant with the CPRA. These audits help identify non-compliance issues and enforce corrective actions.
Provide Guidance: The CPPA provides guidance and resources to help businesses comply with the CPRA. This includes offering best practices, compliance checklists, and other resources to support businesses in meeting their obligations.
Inform Consumers: The CPPA plays a crucial role in informing consumers about their rights and compliance requirements under the CPRA. This helps ensure that consumers are aware of their privacy rights and how to exercise them.
Businesses must ensure that they are compliant with the CPRA and respect consumer rights to avoid enforcement actions by the CPPA. Proactive compliance measures and transparent data-handling practices are essential to mitigate risks and build consumer trust.
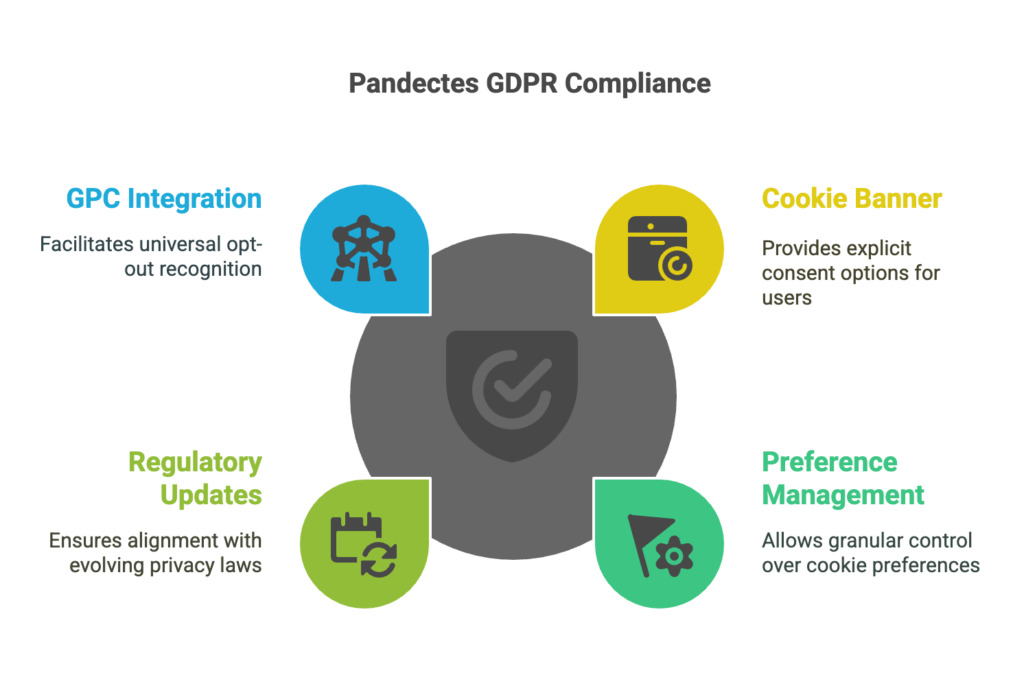
Simplifying Compliance with the Pandectes GDPR Compliance App
For businesses using Shopify, the Pandectes GDPR Compliance app offers an efficient solution for CPRA cookie consent compliance. This app provides:
A CPRA-compliant cookie banner with explicit consent options.
Granular cookie preference management for users.
Automatic updates to align with evolving privacy regulations.
Integration with GPC for universal opt-out recognition.
Using compliance tools like Pandectes can help businesses streamline their cookie consent management and ensure adherence to CPRA regulations.
Conclusion
As data privacy regulations evolve, businesses must prioritize compliance to protect consumer rights and avoid legal repercussions. CPRA requires companies to obtain explicit consent, provide granular opt-out options, and maintain transparency in data collection. By conducting regular audits, updating cookie policies, and implementing CPRA-compliant consent mechanisms, organizations can navigate the complexities of data privacy while fostering consumer trust. Leveraging tools like the Pandectes GDPR Compliance app can further simplify compliance, ensuring businesses stay ahead of regulatory changes in 2025 and beyond.
Staying updated with data privacy laws is crucial to ensure ongoing compliance and protect your business from potential legal issues.



