Introduction
As concerns over online privacy intensify, web technologies are evolving to protect user data better. A significant development in this arena is the introduction of partitioned cookies, also known as Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State (CHIPS). Browsers with CHIPS support offer a new attribute for cookies, known as Partitioned, which enhances privacy. This feature allows for separate cookie jars per top-level site, enhancing user privacy by blocking cross-site tracking. Partitioned cookies ensure that third-party service providers cannot track user behavior across different websites, thereby enhancing user privacy.
Traditional third-party cookies have enabled services to track users across multiple websites, leading to privacy concerns. Partitioned cookies address this issue by ensuring that cookies are only accessible within the same top-level site where they were initially set, thereby preventing cross-site tracking while still supporting essential web functionalities. This allows third-party services to enable services like embedded maps or chat widgets without compromising user privacy.
Cookie Partitioning
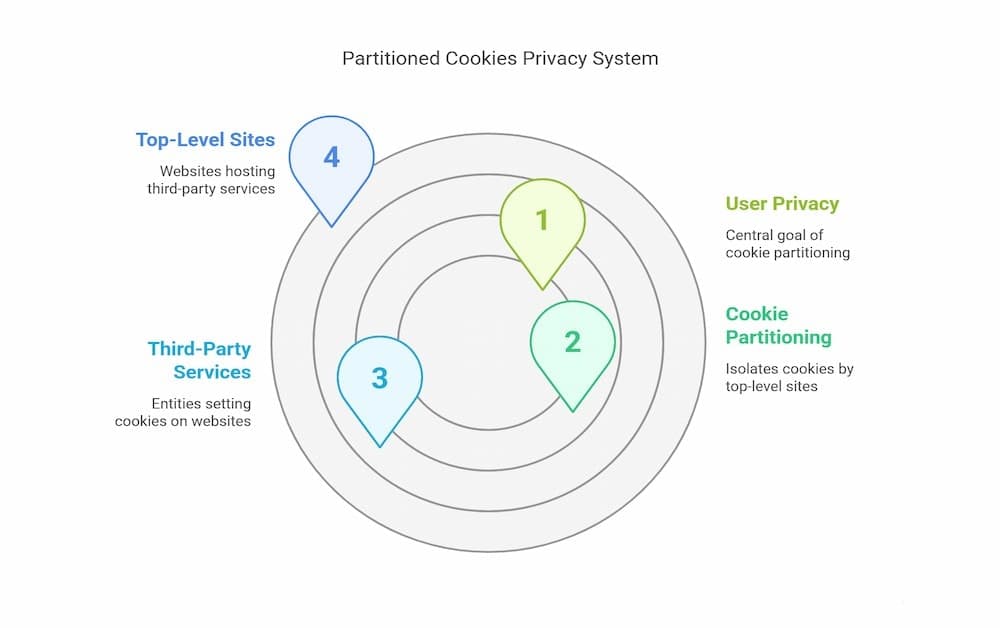
Cookie partitioning is an innovative technique specifically designed to enhance user privacy in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape. It accomplishes this by systematically segregating cookies into distinct storage areas, often referred to as separate cookie jars. These jars are organized based on the top-level site that initiates the creation of the cookies. This method proves highly effective in preventing cross-site tracking, a pervasive practice whereby third-party cookies are utilized to monitor and track users across various unrelated top-level sites, often without their consent.
By employing separate cookie jars, the mechanism of cookies having an independent partitioned state, often abbreviated as CHIPS, ensures that each top-level site maintains its own isolated storage environment for cookies. This level of isolation is critical, as it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive user data, thereby greatly enhancing both user privacy and overall security. Through this effective segregation, users can enjoy a more private browsing experience, knowing that their online activities are less likely to be exposed to unwanted tracking and data collection by third-party entities.
Technical Design
Partitioned cookies are designed to be double-keyed, using both the host key and a partition key. The partition key is derived from the top-level site’s scheme and registrable domain, ensuring that cookies are isolated to the specific context in which they were set. This design creates a separate cookie jar for each top-level site, preventing third-party services from accessing the same cookie across different sites. Browsers can support a new attribute for the Set-Cookie HTTP header, which allows site owners to opt into using partitioned cookies, thereby enhancing privacy by preventing cross-site tracking from third-party service providers.
To implement partitioned cookies, developers can use the new Partitioned attribute when setting cookies. This attribute signals to the browser that the cookie should be stored in a partitioned manner, accessible only within the same top-level site. This cookie set approach ensures that third-party service providers set cookies on a user’s device that are limited to the context in which they were initially set. Additionally, partitioned cookies must be set with the Secure attribute, ensuring they are transmitted only over secure protocols, such as HTTPS. Developers can also use the __Host- prefix to bind cookies to a specific domain or subdomain, adding an extra layer of security.
Security Considerations and Cross-Site Tracking
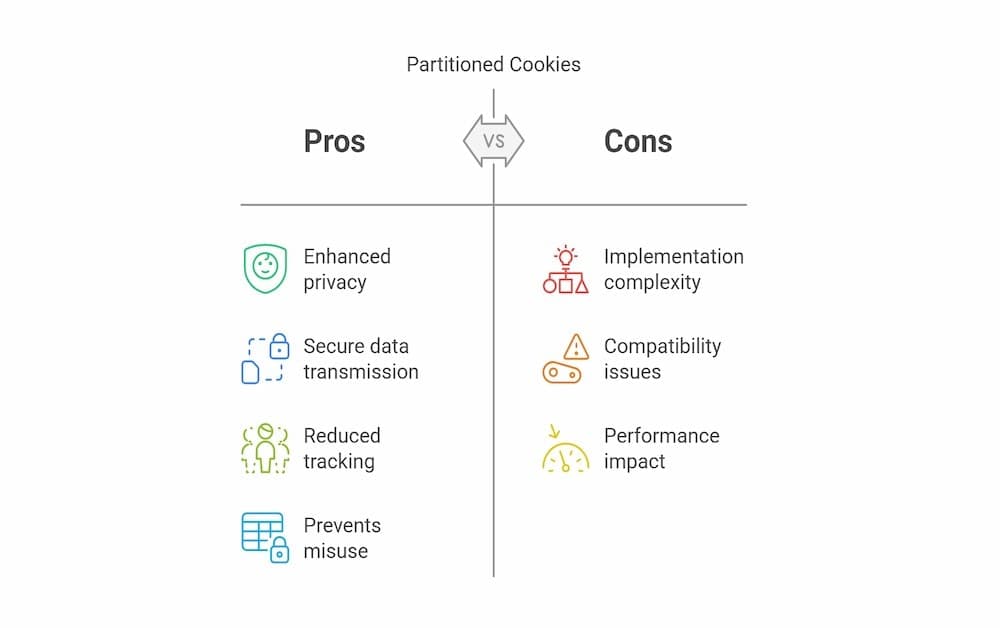
Partitioned cookies enhance security by limiting the scope of cookie access. By implementing partitioned cookies across popular web browsers, they enhance privacy by isolating third-party cookies to prevent cross-site tracking, thus ensuring that users’ data remains confidential and secure while browsing. Since these cookies are only sent in requests that match the partition key, they prevent third-party services from tracking users across unrelated top-level sites. This isolation reduces the risk of potential misuse of personal information and enhances user privacy.
Moreover, by requiring cookies to be set with the Secure attribute and allowing binding to specific domains using the __Host- prefix, partitioned cookies ensure that data is transmitted securely and is less susceptible to interception or unauthorized access. These measures collectively contribute to a more secure web environment.
Benefits of Partitioned Cookies
Partitioned cookies offer several advantages:
- Enhanced User Privacy: By isolating cookies to the top-level site, partitioned cookies prevent cross-site tracking, safeguarding user privacy.
- Support for Legitimate Use Cases: Services like third-party chat widgets, payment processors, and embedded maps can function correctly without compromising user privacy.
- Reduced Risk of Data Misuse: Since cookies are not shared across sites, the potential for misuse of personal information is significantly lowered.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations: Partitioned cookies align with privacy regulations by minimizing the collection and sharing of user data across sites.
How Partitioned Cookies Work
When a user visits a website, any third-party service embedded on that site can set a cookie into partitioned storage on the user’s device. This system, part of the Privacy Sandbox proposals, allows developers to assign cookies to separate storage compartments tied to specific top-level sites, thereby enhancing user privacy by preventing cross-site tracking while still allowing legitimate uses of third-party cookies. This cookie is tied to the top-level site where it was initially set and cannot be accessed from other sites. If the same third-party service is embedded on a different website, it will set a new, separate partitioned cookie specific to that top-level site.
This mechanism ensures that even if a third-party service is present on multiple websites, it cannot use cookies to track users across those sites. Each instance of the service operates within its own partitioned context, maintaining user privacy while still providing necessary functionality.
Google’s Privacy Initiative on Third-Party Cookies
Google launched the Privacy Sandbox initiative aimed at enhancing user privacy while sustaining the viability of online content and services. As part of this initiative, Google introduced CHIPS to allow developers to opt-in to using partitioned cookies. This approach was intended to support cross-site cookies for legitimate use cases while preventing cross-site user tracking.
The privacy sandbox proposal aimed to create a method for managing cookies in a way that enhances user privacy. This proposal allows developers to opt cookies into partitioned storage, ensuring that third-party cookies can only be accessed within the scope of their originating site, thereby restricting cross-site tracking.
However, as of April 2025, Google has officially abandoned its plan to phase out third-party cookies in Chrome, ending its Privacy Sandbox initiative. The decision was influenced by criticism and regulatory scrutiny, with concerns that the initiative continued to track users and raised antitrust issues. Despite this, the concept of partitioned cookies remains a valuable tool for enhancing user privacy.
Implementation Status
The implementation of partitioned cookies varies across browsers:
- Google Chrome: Initially implemented CHIPS as part of the Privacy Sandbox initiative. Despite the abandonment of the broader initiative, the concept of partitioned cookies remains relevant.
- Mozilla Firefox: Has implemented similar features to support partitioned cookies, enhancing user privacy by preventing cross-site tracking.
- Safari: Utilizes Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) to limit cross-site tracking, aligning with the principles of partitioned cookies.
As privacy concerns continue to grow, it is expected that more browsers with CHIPS support will provide new functionalities related to the Set-Cookie HTTP header, allowing site owners to use partitioned cookies for improved privacy and security while managing user tracking across different sites.
Conclusion
Partitioned cookies represent a significant advancement in web privacy, offering a robust solution to the growing concerns surrounding digital tracking and data privacy. By utilizing separate cookie jars for each top-level site, they effectively block cross-site tracking, a common method used by advertisers and other entities to follow users’ online behavior across various websites. This separation of cookies not only enhances user privacy but also minimizes the potential for data leakage between sites, which has been a persistent issue in the realm of internet security.
The design of partitioned cookies enables services to set cookies that remain accessible solely within the same top-level site. This selective accessibility supports a range of legitimate use cases, such as user authentication, session management, and personalization, without compromising user privacy or exposing sensitive information to third parties. As users become more aware of privacy issues and demand greater control over their data, partitioned cookies provide a balanced approach that respects user consent and promotes transparency.
While it’s noteworthy that Google’s broader Privacy Sandbox initiative has been discontinued, the foundational principles underpinning partitioned cookies persist and continue to inspire the ongoing development of innovative privacy-preserving technologies across the web. Developers and organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of adopting these principles in their digital strategies, striving to create environments where user trust is paramount.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace, adopting features like partitioned cookies will be crucial in balancing essential functionality with the pressing need for user privacy. This transition not only aims to enhance the overall user experience but also ensures a safer and more secure online experience for everyone. By prioritizing privacy in design, the tech industry can forge a path toward a future where users feel empowered and protected, ultimately fostering a more secure digital ecosystem.



