Introduction to Facebook Cookies
Facebook cookies are small data files placed on users’ browsers that play a crucial role in shaping the experience on Facebook and across third-party websites. As one of the world’s leading social networking sites, Facebook relies on these cookies to track activity, store unique identifiers, and personalize content for hundreds of millions of Facebook users. Whether you’re browsing your news feed, interacting with friends, or visiting other business services that integrate Facebook features, cookies help deliver tailored content, optimize ad campaigns, and provide measurement reports that inform advertisers and page admins.
For individual users, Facebook cookies enable a more customized experience by remembering ad settings, contact details, and preferences across devices and sessions. They also support security features, such as Facebook Security Help and Instagram Security Tips, which help protect personal messages and account information from unauthorized access. Cookies are essential for analytics services, allowing Facebook and third-party companies to understand user behavior, improve site features, and support research into how people use the platform.
However, the use of Facebook cookies raises important questions about privacy controls and data protection laws. As a data controller, Facebook is required to comply with applicable law, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and guidelines from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States. This means obtaining meaningful consent—or in some cases, explicit consent—before collecting and processing personal data, especially sensitive information such as racial or ethnic origin, trade union membership, or GPS location. Regulatory bodies like the Irish Data Protection Commission closely monitor Facebook’s practices to ensure compliance and protect the rights of affected users.
Facebook users have the ability to manage their privacy through Facebook account settings, adjusting ad settings, and controlling how their data is used for advertising services and other business services. Despite these privacy controls, concerns persist about how Facebook and its third-party partners handle personal data, particularly when it comes to sharing information with third-party companies or tracking users across multiple platforms.
In response to ongoing scrutiny, Facebook has introduced new transparency measures, updated its privacy policies, and expanded security features to better protect individual users. The company regularly publishes measurement reports and collaborates with regulators to address compliance issues. Nevertheless, the debate over Facebook cookies continues, as advocacy groups, regulators, and users weigh the benefits of personalized services against the need for robust data protection and privacy in the digital age.
As Facebook remains a dominant force among social networking sites, its approach to cookies and data protection will continue to shape the broader conversation about privacy, security, and trust online. By providing clear information and empowering users with privacy controls, Facebook can help ensure that its services are both effective and respectful of individual rights under data protection laws.
How Facebook Cookies Work
At their core, Facebook cookies are tiny data files created by Facebook and the Meta Pixel embedded on websites. These cookies gather details like contact details (when provided via forms), GPS location (if enabled), device settings, and even Facebook account information. When a user interacts with ads or clicks on a Facebook page, cookies record this activity. Facebook uses cookies to process information about user interactions to improve services and security, whether on Facebook’s platform or across third-party services. They allow Facebook to tailor ad campaigns, enhance advertising services, and help advertisers provide accurate analytics and measurement reports.
Facebook cookies also play a pivotal role in security. The system uses this cookie data to detect suspicious activity and investigate suspicious logins, enabling Facebook to restrict access, verify accounts, provide Facebook security help, and combat harmful conduct. When unusual patterns are detected, Facebook can require additional authentication to promote safety and protect against account compromise.
Facebook cookies facilitate the seamless integration of relevant features, such as showing Facebook friends who’ve liked a third-party article or enabling seamless login across apps and other sites. They enable social networking integration, such as keeping a user’s news feed updated with friends’ activities. Without these cookies, Facebook’s ecosystem, spanning Messenger, Instagram, and third-party apps, would lose critical functionality.
Technical Aspects of Facebook Cookies
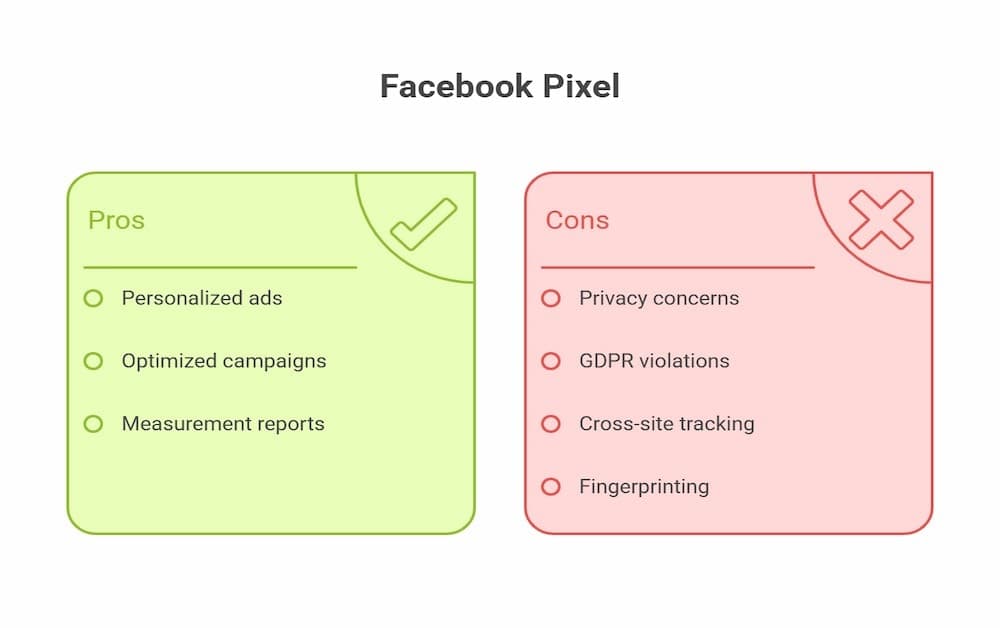
The Facebook Pixel (rebranded as Meta Pixel) is a snippet of code placed on websites that interacts with cookies on users’ devices. It tracks actions like page views, button clicks, and conversions, and also collects device information such as device type and app version, then sends this data back to Facebook for analytics services, personalized ads, and measurement reports. The Pixel’s role in ad campaigns is monumental, allowing advertisers to optimize and retarget ads based on real user behavior.
The Pixel’s cross-site tracking ability means it follows users across multiple domains, even when they leave Facebook and visit search engines or other sites using the same Pixel. This supports consistent ad personalization but also amplifies privacy concerns, especially when data is shared without meaningful consent or when it includes sensitive data types. Notably, Austrian and Irish data protection bodies have flagged GDPR violations related to Meta Pixel usage without explicit consent.
To comply with data protection laws, such as GDPR, Facebook must obtain meaningful consent and potentially offer opt-out mechanisms via browser extensions or built-in cookie consent prompts. Facebook has integrated privacy rules directly into its infrastructure, automating compliance in over hundreds of millions of data transactions.
Third-Party Cookies and Browser Interaction
Third-party cookies set by Facebook on non-Facebook pages enable cross-site tracking. When users visit third-party services or websites that contain Facebook’s infrastructure, such as embedded ads or tracking pixels, their browser sends cookie data to Facebook. This data may also be shared with other partners for analytics or advertising purposes. This third-party service model has been under scrutiny, with many browsers implementing stricter restrictions or offering cookie-blocking features.
Despite these measures, Facebook employs fingerprinting techniques, such as respawning cookies, to maintain tracking continuity even after deletion.
Impact of Facebook Cookies on Users
Cookies collect broad personal data such as device type, IP address, screen resolution, and browsing habits. When combined with third-party information, patterns can emerge that reveal personal tastes, preferences, political views, and demographic attributes. Cookies can also reveal interactions with other users, such as shared content or mutual connections. Privacy researchers have shown that Facebook can infer sensitive attributes, such as race, ethnic origin, or trade union membership, labeling EU users with sensitive interests. Instances exist where over 73% of EU Facebook users were categorized with such interests.
Third Parties and Data Sharing
Third-party companies, from app developers to analytics services, receive cookie-derived insights either through APIs or Facebook login integrations. Information possibly includes personal messages, friends list connections, or high-value photograph metadata. Past incidents, such as Cambridge Analytica, revealed how such systems can exploit user trust and privacy. Data may also be shared in response to legal requests from authorities, where Meta is required to provide certain user information to comply with law enforcement or regulatory demands.
Tracking Beyond Facebook and Across Social Networking Sites
Cookies and the Meta Pixel facilitate tracking users even after they leave Facebook. Data is shared across Instagram, other social networking sites, and search engines. In 2025, the Irish Data Protection Commission flagged the cross-border data flows from the EU to the US without adequate safeguards. This affects users in the European Union and other countries, requiring Facebook to comply with GDPR and provide meaningful consent mechanisms.
Privacy Controls by Users
Facebook allows users to adjust privacy settings in their Facebook settings, including ad preferences, account information, and cookie management. Users can:
- Adjust ad settings (e.g., opting out of certain categories)
- Use ad blockers or browser privacy settings to disable third-party cookies
- Clear cookies and cache from their browser
- Adjust Facebook’s built-in privacy controls to limit personal data usage
Despite these features, the use of consent-or-pay models, which offer an ad-free experience for a fee, has been questioned under the GDPR.
Facebook’s Response to Privacy Concerns
Following scandals like Cambridge Analytica and regulatory fines, Facebook has undertaken policy and technical updates to bolster data protection and transparency. These include:
- Embedding privacy rules in infrastructure through Privacy Aware Infrastructure, safeguarding data at scale.
- Enhancing cookie consent prompts in Europe and offering third-party data controls.
- Strengthening internal policies to combat harmful conduct, detect suspicious activity, verify accounts, and restrict access when needed, including taking action or sharing information based on a good faith belief that it is necessary to comply with the law or protect users, and acting to prevent imminent bodily harm in emergency situations.
- Working with the Irish Data Protection Commission, responding to queries, and adjusting policies to adhere to EU regulations.
- Collaborating with third-party companies, page admins, and app developers to prioritize privacy-by-design frameworks.
Notwithstanding improvements, Facebook continues to face scrutiny regarding consumer protections and rigorous enforcement of data protection laws.
Privacy Protections and Compliance
Under GDPR, Facebook functions as a data controller and processor, requiring meaningful consent to collect or process personal data, especially sensitive categories like racial or ethnic origin. Obligatory measures include:
- Conducting data protection impact assessments
- Employing Privacy by Design principles
- Using Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) for international data transfers
- Offering robust cookie consent frameworks
- Enabling opt-in and opt-out mechanisms for advertising
However, EU regulators in Austria and Ireland have ruled that certain Meta tools, such as the Pixel and login, are illegal without valid consent.
In the US, the Federal Trade Commission penalized Facebook with a $5 billion fine over the Cambridge Analytica scandal. Globally, regulators—including the FTC, Irish Data Protection Commission, and the European Commission—continue to evaluate Facebook’s policies and practices.
Emerging Laws and Browser Changes
In 2025, cookie regulations and privacy expectations are evolving. Consent models and data protections are becoming more stringent, and browser vendors are continuing to block third-party cookies by default. Major platforms, including Chrome, Safari, and Firefox, now offer enhanced anti-tracking settings. In addition, these platforms are introducing new features that give users more control over their privacy.
Site Features and Facebook Cookies
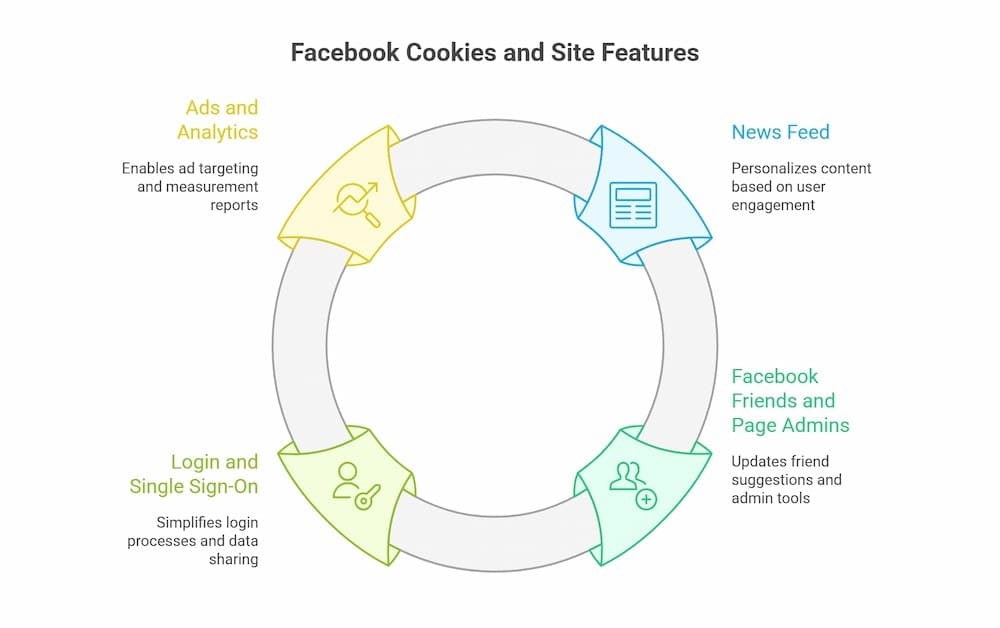
Facebook cookies are essential to key site features, including News Feed personalization, integration with Facebook profiles, Messenger, and Instagram.
- News Feed: Cookies track engagement with posts, ads, friends, and media, enabling tailored feed recommendations.
- Facebook friends and page admins: Cookies update friend suggestions, page notifications, and admin tools.
- Login and Single Sign-On: Cookies simplify login flows and data sharing across Facebook accounts and external sites using Facebook Login.
- Ads and Analytics: Cookies enable ad targeting and measurement report metrics, which are critical to supporting research and page growth.
These features rely heavily on cookies to deliver a seamless user experience. Without them, Facebook’s ecosystem would lose much functionality and integration.
User Data and Facebook Cookies
Facebook cookies collect various personal data points across multiple vectors:
- Browser details: IP address, device type, operating system
- User engagement: Likes, comments, activity on news feed
- Sensitive attributes: inferred preferences including racial/ethnic origin or trade union membership
- Cross-site behavior: visits to other sites with Pixel installed or partner services
- Personal connections: Facebook friends, profile activity, personal messages metadata
This data supports advertising services, analytics services, security features, and measurement reports. Users can navigate their account information via Facebook settings to adjust ad preferences, restrict data sharing, or enable extra security features to verify accounts and detect suspicious activity.
Advertiser Best Practices
Advertisers using Facebook’s advertising services must comply with Facebook’s policies, data protection laws, and privacy expectations. Best practices include:
- Obtain explicit and informed consent from users (meaningful consent) before using Facebook Pixel or similar technologies.
- Provide transparent information about cookie usage and data collection through privacy policies and terms of service.
- Use Facebook’s ad settings to respect user preferences (like opt‑outs).
- Proceed with data minimization and privacy by design to collect only necessary data.
- Conduct periodic data protection impact assessments for campaigns that process sensitive personal data.
- Utilize measurement reports and analytics services responsibly.
- Align with applicable law, such as GDPR (EU), FTC enforcement (US), and other privacy regulations.
By adhering to these practices, advertisers can foster user trust and legal compliance when developing ad campaigns and leveraging Facebook’s advertising services.
Conclusion
Facebook cookies and Meta Pixel are fundamental to how Facebook tracks user behavior, delivers personalized ads, and enhances the user experience across its platform and third-party services. While enabling seamless site features, powerful ad targeting, and security measures, these cookies have raised significant privacy concerns, especially around data collection, cross-site tracking, and the use of sensitive personal data.
Facebook has responded by bolstering cookie consent protocols, investing in privacy-aware infrastructure, and working with regulators to improve data handling and transparency. Nevertheless, global regulators continue to challenge its practices, particularly in the European Union and by the Irish Data Protection Commission.
For individual users, understanding how cookies operate is essential. Through Facebook settings, ad controls, and browser-based cookie management, users can limit tracking and protect their personal data. Advertisers, too, must implement transparent, consent-based approaches and prioritize compliance.
As digital cookie landscapes evolve, with browsers phasing out third-party cookies and privacy laws strengthening, it’s vital for all stakeholders, including Facebook, advertisers, app developers, and individual users, to champion meaningful consent and privacy protections. In doing so, Facebook can rebuild trust, operate within privacy rules, and comply with data protection regulations worldwide, including those enforced by bodies like the Irish Data Protection Commission and the European Union.