Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, the protection of personal data has become paramount. The Philippines, recognizing the importance of data privacy, enacted the Data Privacy Act of 2012 (Republic Act No. 10173), commonly referred to as the PDPA. As a privacy law, the PDPA establishes strict guidelines for organizations regarding the collection, consent, security, and responsible handling of personal data. This comprehensive legislation aims to safeguard personal information and ensure that entities handle data responsibly. For a look at similar legislation in Sri Lanka, see their Personal Data Protection Act.
The PDPA applies to all organizations, both public and private, that process personal data. This means it covers any entity that processes personal data, including government agencies, corporations, and even small businesses. To ensure compliance, the law mandates the appointment of a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who oversees data protection measures within the organization. The DPO plays a crucial role in implementing appropriate security measures, managing data breaches, and ensuring that data subjects’ rights are upheld.
The significance of the PDPA extends beyond mere compliance; it is a commitment to maintaining the trust of individuals whose personal data is being handled. In the event of data breaches, organizations are required to notify affected individuals and the National Privacy Commission within a certain timeframe, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Furthermore, the PDPA empowers individuals with rights such as the right to access their personal information, the right to rectify inaccuracies, and the right to object to the processing of their data. These rights equipped individuals with the tools to take charge of their personal information, fostering a culture of respect for privacy.
Moreover, the law emphasizes the need for organizations to conduct regular data protection impact assessments. This proactive measure helps identify potential risks to personal data and implement strategies to mitigate those risks. Training and awareness programs for employees concerning data privacy are also essential to cultivate a culture of privacy within organizations, making everyone accountable for data protection. The PDPA sets strict guidelines for data collection, consent, and security, requiring organizations to adhere to detailed requirements to ensure responsible data handling.
The PDPA is not just a legal framework; it is a vital step towards creating an environment where personal data is treated with the utmost respect, emphasizing the importance of transparency, accountability, and individual rights in the face of rapid technological advancements. The core principles of the PDPA serve as the foundation for lawful and ethical data processing. As digital interactions continue to grow, the adherence to these principles will be crucial in navigating the complexities of modern data privacy challenges. For a deeper understanding of similar legislation, you can read an overview of India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA).
Understanding the PDPA
The key principles of the Philippine Data Privacy Act (PDPA) serve as the foundation for compliance, guiding organizations in protecting personal data and building trust with stakeholders.
The PDPA outlines specific responsibilities for data controllers and processors. Data controllers determine the purpose and means of processing personal data and have legal obligations regarding notification of personal data breaches, managing data subject rights, and ensuring lawful processing. Data processors handle data on behalf of controllers. Both entities are required to implement data protection measures to ensure compliance with the law. This includes obtaining consent from data subjects before processing their personal data, ensuring responsible data collection as guided by the PDPA, ensuring data accuracy, and establishing data retention policies.
Access controls are a critical component of data protection. Organizations must implement measures such as multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. Effective access management is essential for controlling and restricting access to personal data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can handle such information. Regular audits and risk assessments should be conducted to identify potential vulnerabilities in data processing activities. Additionally, organizations must ensure that personal data is not retained longer than necessary, aligning with the principle of data minimization.
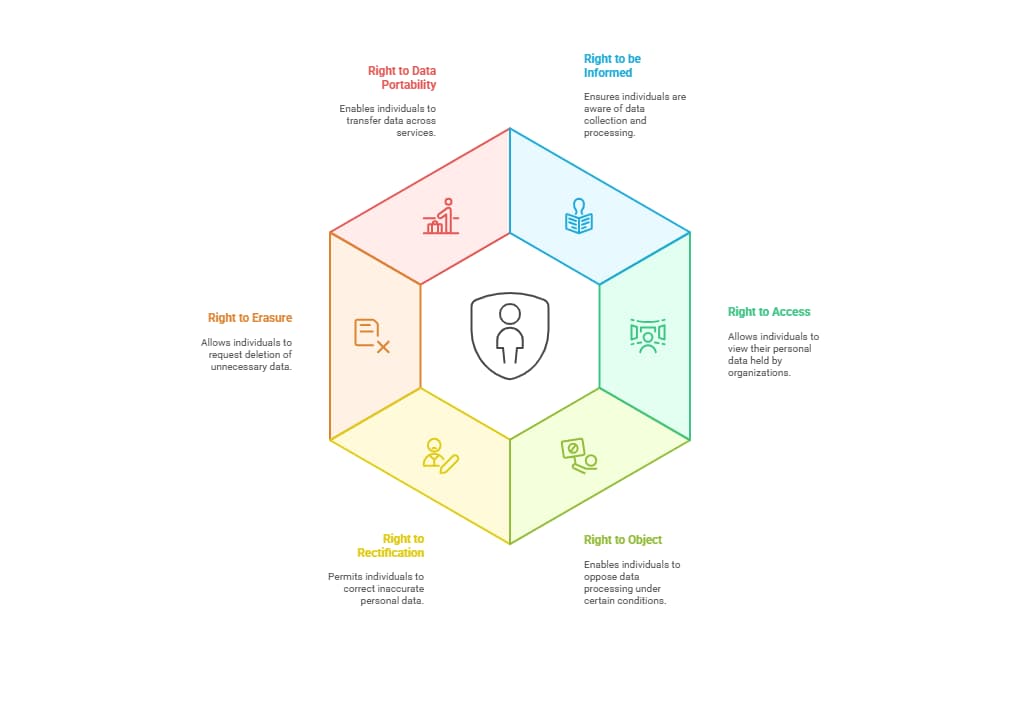
Data Subject Rights
Under the PDPA, data subjects are granted specific rights to protect their personal information. These rights empower individuals to have control over their data and include:
- Right to be Informed: Data subjects must be informed about the collection and processing of their personal data, including the purpose and scope.
- Right to Access: Individuals have the right to access their personal data held by an organization.
- Right to Object: Individuals have the right to challenge the processing of their personal data in specific situations, including for direct marketing activities.
- Right to Rectification: Individuals can request corrections to inaccurate or outdated personal data.
- Right to Erasure or Blocking: Data subjects can request the deletion or blocking of their personal data, especially if it’s no longer necessary for the purpose it was collected.
- Right to Data Portability: Individuals can obtain and reuse their personal data across different services.
Organizations must establish clear procedures for handling data subject requests and ensure timely responses. Failure to uphold these rights can lead to non-compliance penalties and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Compliance Requirements
To ensure compliance with the PDPA, organizations must implement a comprehensive privacy management program. This program should outline key responsibilities and processes for handling personal data. Data mapping is essential to identify the types of personal data processed and the purposes for which it’s used. This helps in understanding data flows and identifying areas that require additional security measures. When entering into data sharing agreements, organizations must ensure that adequate safeguards are in place to protect the rights of data subjects and comply with legal requirements.
Data protection practices must be established to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data. This includes implementing organizational, physical, and technical security measures. Organizations should also have data breach management procedures in place to respond to security incidents promptly. Regular audits and risk assessments are crucial to evaluate the effectiveness of data protection measures and ensure ongoing compliance with the PDPA.
Data Handling and Protection
Handling personal data responsibly is at the core of the PDPA. Organizations must implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction. It is essential to protect data by using suitable technical and organizational measures to avoid penalties and maintain credibility. Sensitive personal information, such as financial records or medical history, requires additional safeguards due to the potential harm that could result from a breach.
Data processors, who handle data on behalf of controllers, must be contractually obligated to protect personal data and ensure compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). In some cases, processing may be permitted without consent if there is a legal obligation to do so, such as compliance with regulatory requirements. Organizations should establish procedures for reporting data breaches to the National Privacy Commission and affected data subjects promptly. Regular reviews and updates of data protection measures are necessary to adapt to evolving threats and technological advancements.
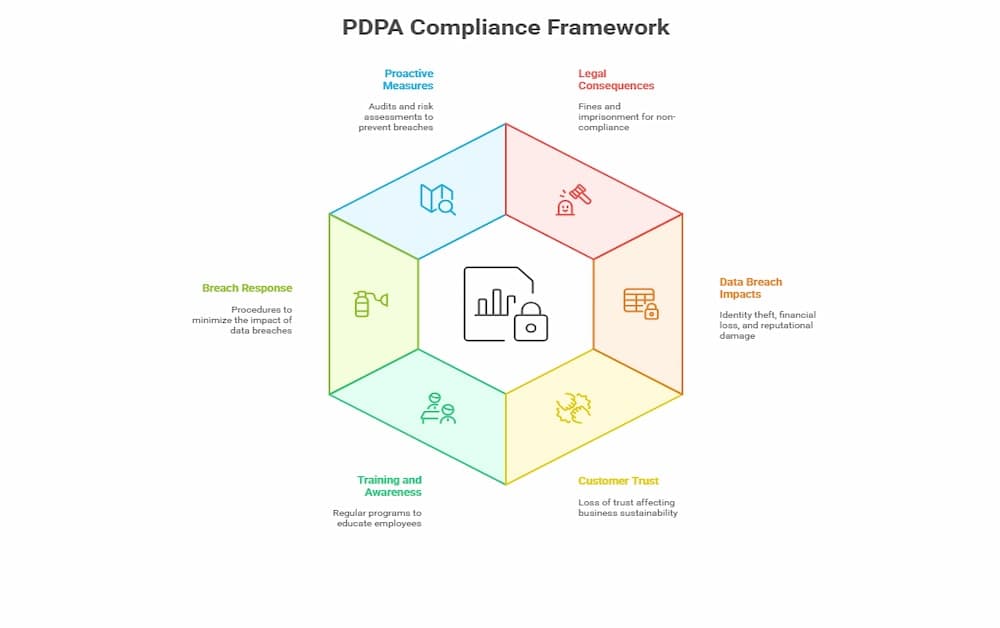
Risks and Consequences
Non-compliance with the PDPA can result in severe consequences for organizations. Penalties include fines and potential imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation. Unauthorized processing of personal data is a specific offense under the PDPA and can lead to significant legal consequences, including both imprisonment and fines. Data breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and damage to an organization’s reputation. Beyond legal repercussions, organizations may lose customer trust, which can have long-term impacts on business sustainability.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must conduct regular training and awareness programs to ensure that employees understand the importance of data protection and security. Establishing clear procedures for responding to data breaches and minimizing their impact is also essential. Proactive measures, such as regular audits and risk assessments, can help identify potential vulnerabilities and prevent data breaches before they occur.
Ensuring Compliance
Ensuring compliance with the PDPA requires a data-centric approach to security. Organizations must establish a culture of data protection, where all employees understand their roles and responsibilities in safeguarding personal data. Regular monitoring and review of data protection practices are necessary to ensure they remain effective and adapt to changing regulatory expectations.
Staying up to date with changes to the PDPA and other relevant privacy laws is crucial. Organizations should establish a privacy program to oversee compliance efforts and ensure that personal data is protected. Privacy professionals play a key role in managing compliance with privacy laws and facilitating data subject rights within such programs. This program should include regular training, policy updates, and mechanisms for monitoring compliance across all departments.
Understanding Privacy Regulations
The PDPA is a key regulation that organizations must comply with when processing personal data in the Philippines. Data processing should only occur for a legitimate purpose as outlined by law, ensuring that any processing is permitted only when aligned with a recognized and lawful objective. However, other privacy laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), may also apply to organizations that process personal data across borders. Understanding the interplay between these regulations is essential for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Organizations must stay informed about regulatory expectations and changes to privacy laws to ensure compliance. Establishing procedures for responding to data breaches and minimizing their impact is critical. A comprehensive privacy program should be in place to oversee compliance with privacy regulations and ensure that personal data is protected effectively.
Conclusion
Ensuring compliance with the Philippine Data Privacy Act (PDPA) is vital for organizations seeking to protect personal data and maintain customer trust. Simplifying PDPA compliance can be achieved through a multi-faceted approach that includes a thorough understanding of the law’s requirements and effective implementation of data protection measures.
To begin with, organizations should prioritize appointing a dedicated Data Protection Officer (DPO) who is well-versed in the intricacies of the law. The DPO’s role is crucial as they serve as the primary point of contact for privacy-related matters and oversee data protection strategies. Regular training for employees on data privacy principles can further strengthen the organization’s defenses against data breaches and violations.
Additionally, conducting regular audits and assessments of data handling practices allows organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities and rectify them proactively. These audits provide key insights into how data protection practices are working, such as detecting configuration changes, software installations, and access to sensitive data, which helps improve compliance and security by identifying privilege abuse and other risks. It is essential for organizations to stay updated on any regulatory changes that may impact their operations, as this ensures ongoing compliance and adaptability to new requirements.
A culture of privacy should permeate the organization, encouraging all employees to take responsibility for the personal data they manage. This cultural shift can be fostered through awareness campaigns and individual accountability.
Ultimately, the responsible handling of personal data not only fulfills the legal obligations set forth by the PDPA but also plays a significant role in building customer trust. When customers feel confident that their data is in safe hands, they are more likely to engage with and support the business. This trust can lead to enhanced customer loyalty, which is integral to long-term business success in today’s competitive landscape. By establishing a robust data protection framework, organizations not only comply with the law but also position themselves for sustainable growth and success in the future.



