Introduction
The evolving landscape of data privacy regulation in California continues to push businesses to reexamine how they handle personal information. As the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) builds on the foundations of the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), organizations are now required to adhere strictly to the data minimization principle. In 2025, companies must ensure they only collect, process, and store personal data that is truly necessary for their operational purposes. This focus on data minimization not only helps protect sensitive personal information and consumer data but also reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
With consumers increasingly demanding greater transparency and control over their personal information, compliance with the CPRA has never been more critical. Enhanced consumer rights, such as the ability to correct inaccurate personal information, opt out of excessive data collection, and request data portability, have set a high bar for data controllers. Furthermore, regulatory scrutiny from bodies like the California Privacy Protection Agency reinforces the need for robust data protection practices and stringent internal controls to ensure ongoing compliance with data privacy regulations.
Understanding CPRA Data Minimization
CPRA data minimization emphasizes that businesses must only collect the personal data necessary to fulfill specific, legitimate purposes. This concept not only aligns with global standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) but also complements California’s stringent data privacy laws. The idea is simple: by reducing the amount of personal information collected, companies can minimize exposure to risks related to data breaches, unauthorized sharing, and storage limitations. Organizations are expected to maintain a comprehensive data inventory and implement measures to protect personal information while ensuring compliance with legal obligations.
Beyond just reducing data volume, the CPRA encourages businesses to continuously assess their data processing operations and implement corrective measures when excessive data is collected. In 2025, this means implementing regular data protection assessments, risk assessments, and data protection impact assessments to monitor compliance. The emphasis on data minimization supports not only privacy and data protection but also fosters consumer trust by ensuring that consumer rights, such as restricting processing and opting out of cross-context behavioral advertising, are fully respected.
Data Inventory and Mapping
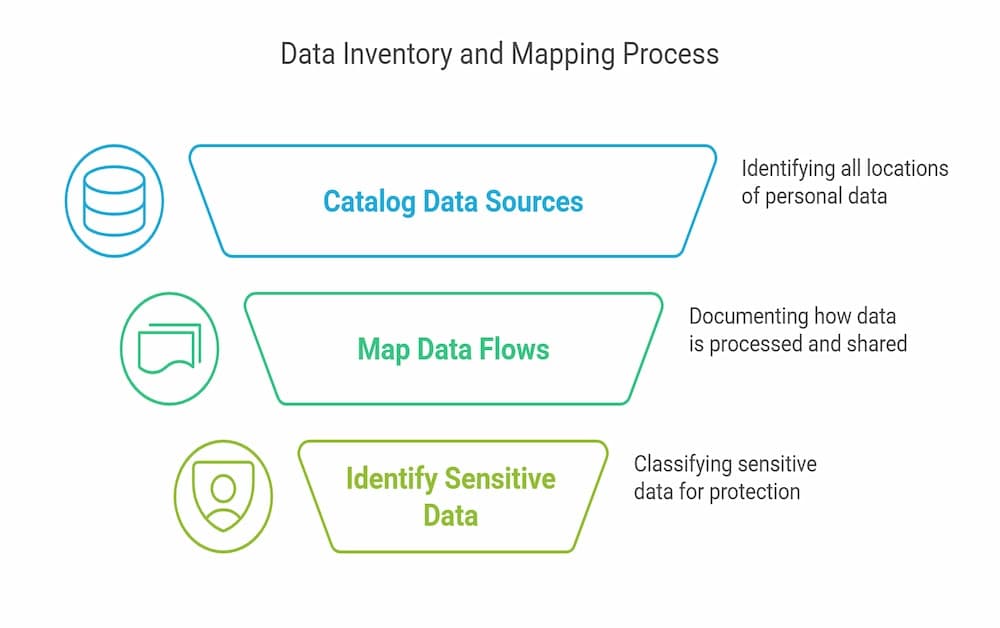
Conducting a comprehensive data inventory and mapping exercise is a critical first step in achieving CPRA compliance. Organizations need to document every piece of personal data collected—from health data to financial information—and establish clear records of data processing activities. A well-maintained data inventory provides visibility into where personal information is stored and how it is processed and identifies potential areas of excessive data collection. This detailed map is essential for pinpointing inefficiencies in data storage and ensuring that storage limitation principles are followed.
To effectively perform a data inventory and mapping exercise, businesses should consider using automated tools and standardized procedures. Key steps include:
Cataloging Data Sources: Identify all locations where personal data is stored, including digital databases, electronic documents, and cloud storage.
Mapping Data Flows: Document the flow of personal data collected from California residents, detailing how data is processed, shared, and stored.
Identifying Sensitive Data: Classify sensitive personal information and consumer data to ensure that data protection measures are in place for sensitive data categories. This process not only supports ongoing compliance but also provides a framework to respond efficiently to consumer requests, such as data access or correction of inaccurate personal information.
Data Collection and Purpose Limitation
One of the cornerstones of CPRA compliance is the clear definition and limitation of data collection purposes. Organizations must establish and document the specific reasons for which they collect personal data, ensuring that data collection practices are both transparent and justifiable. By limiting data collection to what is reasonably necessary for achieving specified business objectives, companies not only protect consumer privacy but also mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized data processing.
Updating privacy policies and internal documentation is essential to meet the CPRA’s requirements. Businesses should clearly state how consumer data is processed and restrict data processing operations to disclosed and necessary activities. Key actions include:
Defining Data Collection Purposes: Establish clear, documented purposes for collecting consumer data, including compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act and other regulatory mandates.
Limiting Data Collected: Ensure that personal data collected is limited to what is necessary, and avoid excessive data collection practices that may lead to non-compliance.
Documenting Processing Activities: Keep detailed records of how each category of data is used, shared, or processed, and regularly update these records to reflect any changes. This rigorous approach to data collection and purpose limitation strengthens consumer consent frameworks and ensures that businesses remain aligned with both CPRA and broader data protection requirements.
Data Storage and Retention
Effective data storage and retention policies are fundamental to protecting consumer privacy and ensuring CPRA compliance. Companies must develop a clear retention schedule that specifies the duration for which each category of personal data will be stored. This retention schedule should be guided by the principles of proportionality and storage limitation, ensuring that data is retained only for as long as it is necessary to fulfill its intended purpose. Regular reviews of retention policies are crucial, especially in a dynamic regulatory environment like 2025, where data breaches and data protection impact assessments can reveal potential vulnerabilities.
In addition to establishing clear retention policies, organizations should implement automated data deletion processes to minimize the risk associated with outdated or excessive stored data. Important considerations include:
Regular Data Reviews: Conduct periodic audits to ensure stored data remains relevant and necessary.
Anonymization and Deletion: Establish procedures for deleting or anonymizing personal data that is no longer needed, particularly for sensitive personal information and consumer data.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that data retention policies comply with legal obligations, such as those related to financial institutions or health data. By implementing these strategies, companies can maintain data integrity and reduce the potential for data breaches, thereby protecting both consumer rights and overall data protection practices.
Consent Management and Consumer Rights
A robust consent management framework is essential for meeting CPRA requirements and ensuring that consumers have meaningful control over their personal information. Effective consent management not only covers the collection and processing of personal data but also empowers consumers to exercise their rights, such as accessing, correcting, or deleting their personal data. This system must be integrated into every stage of data processing—from the moment personal data is collected to its eventual deletion or anonymization.
To facilitate a strong consent management process, businesses should consider:
Implementing User-Friendly Consent Tools: Provide clear options for consumers to opt out of data collection or cross-context behavioral advertising.
Establishing Clear Communication Channels: Ensure consumers can easily submit requests to correct inaccurate personal information, access their data, or restrict processing activities.
Employee Training: Regular training sessions on data privacy and consent management best practices are essential, especially in sectors like financial institutions and healthcare. These measures not only support compliance with the CPRA and the California Consumer Privacy Act but also foster trust among consumers by ensuring their data is processed in a transparent, secure, and compliant manner.
Third-Party Data Minimization Obligations
The responsibility for CPRA compliance extends beyond internal operations to include any third parties involved in processing consumer data. Whether working with contractors, service providers, or vendors, businesses must ensure that these partners adhere to the same data minimization principles mandated by the CPRA. This involves the implementation of rigorous Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) and regular vendor assessments to verify that all parties handle personal data with the appropriate level of care and security.
When managing third-party relationships, organizations should adopt several best practices:
Vendor Assessments: Regularly review third-party data processing activities to ensure they align with CPRA standards.
Comprehensive DPAs: Draft and enforce agreements that outline clear expectations regarding data collection, retention, and processing activities.
Monitoring and Auditing: Establish protocols to periodically audit the data protection practices of service providers to safeguard consumer data and sensitive data. By integrating these measures, businesses can effectively reduce the risk of non-compliance and ensure that consumer data remains protected even when shared with external partners. This also reinforces the broader data privacy ecosystem, supporting ongoing compliance with both CPRA and related data protection regulations.
CPRA Compliance Checklist
A detailed CPRA compliance checklist is an invaluable tool for businesses striving to meet the rigorous requirements of the CPRA and the California Consumer Privacy Act. This checklist should serve as a step-by-step guide, enabling organizations to systematically address each aspect of data minimization, consent management, data storage, and third-party data processing. With a comprehensive CPRA compliance checklist, businesses can better ensure that every data protection measure—from risk assessments to the implementation of security measures—is properly addressed.
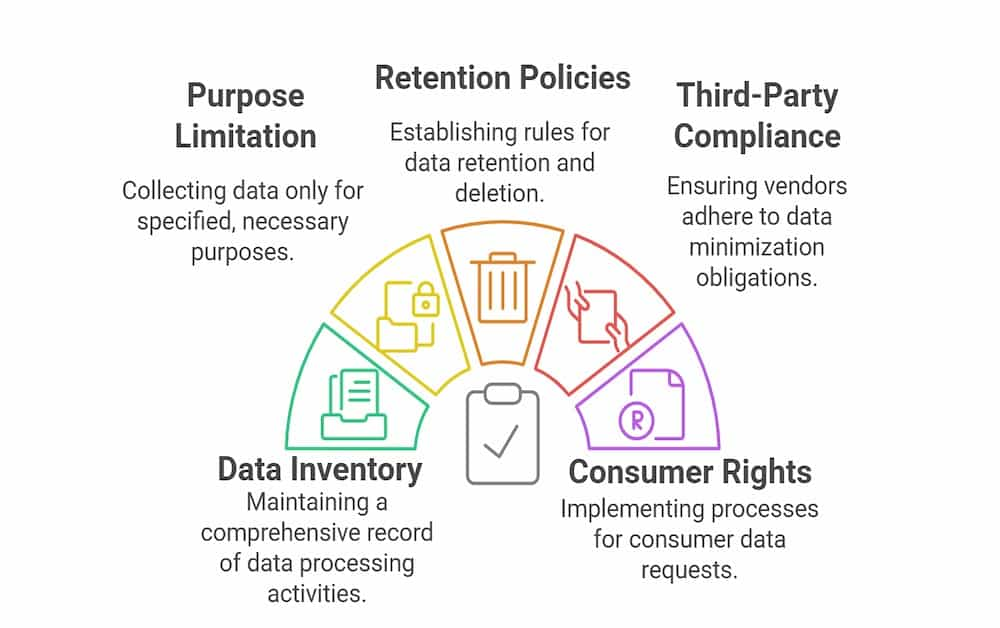
Key components of a CPRA compliance checklist include:
Data Inventory and Mapping: Verify that a comprehensive data inventory is maintained and that all data processing operations are documented.
Purpose Limitation and Data Collection: Ensure that data collection is limited to what is necessary for disclosed purposes and that consumer consent is obtained and documented.
Retention and Deletion Policies: Establish clear data retention policies and automate the deletion or anonymization of outdated personal data.
Third-Party Compliance: Confirm that all third parties, including contractors and vendors, adhere to the CPRA’s data minimization obligations.
Consumer Rights and Requests: Implement robust processes for handling consumer requests related to data access, correction of inaccurate personal information, and opt-out from data sales. This systematic approach not only aids in achieving CPRA compliance but also reinforces the broader commitment to privacy and data protection practices that safeguard consumer rights and ensure ongoing regulatory adherence.
Data Privacy Regulations and Enforcement
In 2025, data privacy regulations continue to evolve with increasing regulatory scrutiny and enforcement actions. The California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) plays a central role in enforcing CPRA mandates, conducting audits, and investigating potential data breaches or instances of excessive data collection. The CPPA’s authority is complemented by the enforcement capabilities of the California Attorney General, both of which are committed to protecting consumer privacy and ensuring that businesses adhere strictly to the established data protection requirements.
The enforcement environment is characterized by significant penalties for non-compliance, with fines reaching up to $7,500 per intentional violation. This strict regulatory framework underscores the importance of proactive data protection measures, including comprehensive data inventories, regular data protection impact assessments, and robust risk assessments. By adhering to these practices, businesses not only mitigate the risk of financial penalties but also uphold the trust of their customers by ensuring that consumer data and sensitive personal information are managed securely and in accordance with both CPRA and other relevant data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation.
Consumer Privacy and Data Protection
At its core, the CPRA reinforces consumer rights by granting individuals significant control over their personal information. Consumers now have the right to know what personal data is collected, the purposes for its collection, and the processing activities involved. This enhanced transparency empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their consumer data and to take action if their privacy is compromised. For instance, consumers can request access to their personal information collected by data controllers, opt out of the sale of personal data, or correct inaccurate personal information, thus ensuring that their sensitive data remains accurate and secure.
Moreover, the CPRA mandates that businesses protect consumer privacy by implementing robust data protection measures. These measures include:
Security Measures: Adopt advanced security protocols to protect stored data and prevent data breaches.
Data Protection Impact Assessments: Regularly evaluate the risks associated with data processing activities, especially for sensitive data such as health data and financial information.
Data Portability and Transparency: Ensure that consumers can easily transfer their data or obtain a copy of their personal data in a portable, readily usable format. These practices not only fortify the overall data protection framework but also align with international standards and foster an environment where consumer privacy is respected and protected.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of CPRA compliance in 2025, the importance of data minimization cannot be overstated. Businesses that implement robust data inventory and mapping exercises, clearly define and limit data collection purposes, and adhere to strict data storage and retention policies will be well-positioned to meet the regulatory demands of the CPRA and the California Consumer Privacy Act. By focusing on data protection assessments, risk management, and consumer consent frameworks, organizations can ensure that they not only comply with legal obligations but also build consumer trust and protect sensitive personal information.
In summary, achieving CPRA compliance requires a strategic and comprehensive approach that spans multiple aspects of data privacy—from the careful management of consumer data to the strict enforcement of data minimization practices. With detailed CPRA compliance checklists, enhanced consent management solutions, and vigilant third-party monitoring, businesses can secure personal information, reduce the risk of data breaches, and maintain ongoing compliance with data privacy regulations. As companies continue to evolve their data protection practices, the commitment to privacy and data integrity will remain at the forefront of responsible business operations in 2025 and beyond.



